Question
Question: How do you verify experimentally the focal length of the convex lens is increased when it is kept in...
How do you verify experimentally the focal length of the convex lens is increased when it is kept in water?
Solution
If to a certain height the lens is dipped which is greater than the focal length of the lens in the air than that image would be clearly visible therefore, the focal length of the lens will increase in the water.
Complete step-by-step answer :
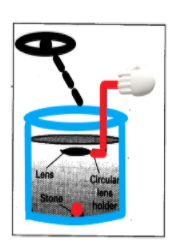
Material required to verify this experimentally are:
- Convex lens
- Tumbler
- Water
- Circular lens holder
- Stone
The steps given below will verify this experiment are:
STEP 1: Take the lens (convex lens) of focal length and the tumbler whose height is known and is four times the focal length of the lens.
STEP 2: Put the stone into the tumbler and pour some water to the level where the height of the level should be greater than the focal length of the lens.
STEP 3: Now you can dip the lens (convex lens) horizontally by using the lens holder.
STEP 4: Now set the distance between the lens (convex lens) and the stone in such a way that the distance is equal or less than the focal length of the lens.
STEP 5: After step 4, look that stone through the lens, you will notice that the stone is visible at this stage.
STEP 6: Now slowly it seems to be increasing the distance between the lens and the strone.
STEP 7: Now at the final step we can see that as soon as the distance gets greater than the focal length the stone will not be visible anymore.
Therefore, the focal length of the lens will increase in the water.
Note : Focal length is said to be the distance between the centre of convex lens or a concave mirror and a focal point of that lens or mirror i.e. - the point where the parallel rays of light meet or we can say converge.
