Question
Question: How do you solve the inequality\[\dfrac{1}{{x + 1}} \succ \dfrac{3}{{x - 2}}?\]...
How do you solve the inequalityx+11≻x−23?
Solution
The given question describes the operation of addition/ subtraction/ multiplication/ division. In this question, we have to find the value ofx. At first, we would arrange the fraction terms to one side. After that, we have to find the final condition to find the value x. In this question, we have to use a number line to assume the value ofx and compare it with the final condition.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question, we have to solve the following inequality terms,
x+11≻x−23
First, we have to arrange the fraction terms into one side of the equation. So, the above
equation can also be written as,
Using cross-multiplication, we get
(x−2)(x+1)(3(x+1))−(1(x−2))≺0 (x−2)(x+1)3x+3−x+2≺0Let’s solve the numerator using arithmetic operations,
(x−2)(x+1)3x+3−x+2≺0 (x−2)(x+1)2x+5≺0So, the final condition is,
\dfrac{{2x + 5}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x + 1} \right)}} \prec 0$$$$ \to \left( 1 \right)
For finding the value ofx we have to assume,
(Case: 1) 2x+5=0
(Case: 2) x−2=0
(Case: 3) x+1=0
In case: 1 we get,
2x+5=0 2x=−5 x=2−5In case: 2 we get,
x−2=0 x=2In vase: 3 we get,
x+1=0 x=−1So finally we have,
x=2−5,x=2andx=−1
Let’s mark the above-mentioned values in the number line,

We have three options forxvalue. Now we need to find the correctxvalue among the three answers. Here we have intervals (−∞,2−5),(2−5,−1),(−1,2)and(2,∞)
To find the correct interval we have to assume anyone value with each interval and substitute that value in the equation(1)
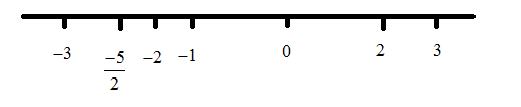
In the interval (−∞,2−5) we assume−3. So, the final
condition(1)becomes,
(1)→(x−2)(x+1)2x+5≺0
Where, x=−3
(−3−2)(−3+1)2(−3)+5≺0
(−5)(−2)−6+5≺0
10−1≺0
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval(2−5,−1), we assume x=−2
(1)→(x−2)(x+1)2x+5≺0
(−2−2)(−2+1)2(−2)+5≺0
−1×−4−4+5≺0
41≺0
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
In the interval(−1,2), we assumex=0
(1)→(x−2)(x+1)2x+5≺0
(0−2)(0+1)2(0)+5≺0
2−5≺0
The above equation satisfies the condition.
In the interval(2,∞), we assumex=3
(1)→(x−2)(x+1)2x+5≺0
(3−2)(3+1)2(3)+5≺0
4×16+5≺0
411≺0
The above equation doesn’t satisfy the condition.
So, the final answer isx∈(−∞,(2−5))∪(−1,2)
Note: The total limit of the number line is(−∞,+∞). In this type of question we should use the arithmetic operation of addition/ subtraction/ multiplication/ division/ cross multiplication. Take care when assuming the value ofxin the number line. If thexvalue is a fraction number, convert it into a decimal number for easy calculation.
