Question
Question: How do you increase the voltage of the voltmeter?...
How do you increase the voltage of the voltmeter?
Solution
Voltmeter is an instrument that measures the voltage or potential difference of volts of either direct or alternating electric current. Voltmeter works on the principle that torque is generated by the current which is induced due to voltage measurement. The torque deflects the pointer of the voltmeter which is directly proportional to the potential difference between volts. The voltmeter is always connected with a circuit parallel. By increasing the resistance, the range of the voltmeter can be increased. With the help of resistance connecting in series with a voltmeter.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know the way to increase the range of a voltmeter, we need to connect a suitable high multiplier resistance in series with a voltmeter.
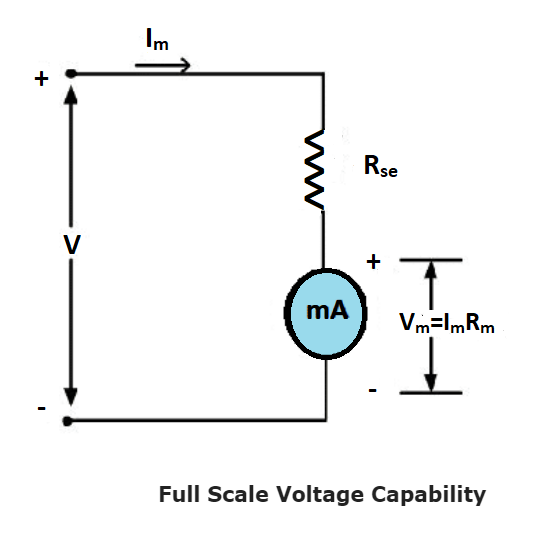
The series resistance is given by Rse=Rm(VmV−1)
Where Vm=ImRm (Im= full scale current)
And, the required voltmeter range isV, Voltmeter range is Vm and meter internal resistance isRm.
Voltage sensitivity is the reciprocal of the necessary current for full-scale deflection.
Voltage sensitivity=Im1Ω/volt
To get the larger voltage sensitivity the meter current needs to be smaller. The resistance of the voltmeter is equal to the sensitivity times the complete voltage.
Note:
The DC voltmeter has polarity signs on it. One has to connect the plus (+) terminal, the higher point of potential of the voltmeter and the minus (−) terminal, the lower point of potential of the voltmeter to obtain a meter deflection
There are no polarity signs on the AC voltmeter and can be connected anyways. There are three types of voltmeter: analog voltmeter, digital voltmeter and vacuum tube voltmeter.
