Question
Question: How do you find the limit of \(\dfrac{\left| x+2 \right|}{x+2}\) as \(x\) approaches \(-2\)?...
How do you find the limit of x+2∣x+2∣ as x approaches −2?
Solution
In this problem we need to calculate the limit value of the given function at given x value. For this we will first check whether the given function exists at the limit value or not at a given x value. So, we will first calculate the limit from the left at given x value and the limit from the right at given x value. For this we will write first define the given function by using the known function definition \left| x \right|=\left\\{ \begin{matrix} x,\text{ if }x\ge 0 \\\ -x,\text{ if }x<0 \\\ \end{matrix} \right.. We will this function definition to define the function ∣x+2∣. After defining the function, we will calculate the right-hand limit and left-hand limit and then we will conclude the problem by comparing both the values.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given function, x+2∣x+2∣.
We know that the value of the function ∣x∣ is
\left| x \right|=\left\\{ \begin{matrix}
x,\text{ if }x\ge 0 \\\
-x,\text{ if }x<0 \\\
\end{matrix} \right.
From the above definition, the value of the function ∣x+2∣ will be
\left| x+2 \right|=\left\\{ \begin{matrix}
x+2,\text{ if }x\ge -2 \\\
-\left( x+2 \right),\text{ if }x<-2 \\\
\end{matrix} \right.
Given that x approaches −2.
Calculating the left-hand side limit or limit from the left-hand side.
Left hand side limit means the value of x is less than −2 i.e., x<−2.
If x<−2 the value of the function ∣x+2∣ is
∣x+2∣=−(x+2)
From the above value the value of the given function x+2∣x+2∣ will be
x+2∣x+2∣=x+2−(x+2)⇒x+2∣x+2∣=−1
Applying the left-hand limit to the given function, then we will get
x→−2−limx+2∣x+2∣=x→−2−lim−1⇒x→−2−limx+2∣x+2∣=−1
Calculating the right-hand limit or limit from the right hand side.
Right hand side limit means x>−2.
If x>−2 the value of the function ∣x+2∣ is
∣x+2∣=x+2
From the above value the value of the given function x+2∣x+2∣ will be
x+2∣x+2∣=x+2x+2⇒x+2∣x+2∣=1
Applying the right-hand limit to the given function, then we will get
x→−2+limx+2∣x+2∣=x→−2+lim1⇒x→−2+limx+2∣x+2∣=1
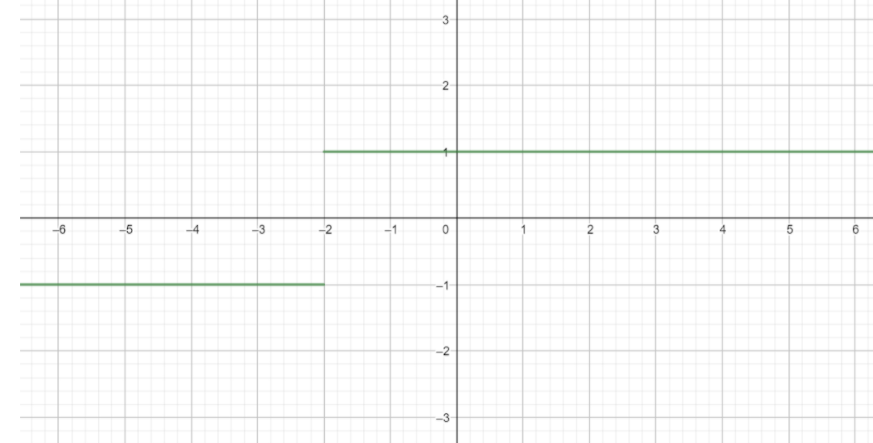
Here we have x→−2+limx+2∣x+2∣=x→−2−limx+2∣x+2∣. So, the limit of the function doesn’t exist.
Note: We can clearly observe that the function is simply y=1 for x>−2 and y=−1 for x<−2. So, we can’t calculate the limit of the function. We can also observe this in the graph of the given equation which is shown in below figure