Question
Question: How do you find the length of a curve in calculus?...
How do you find the length of a curve in calculus?
Solution
The length of a curve represented by a function, y=f(x) can be found by differentiating the curve into a large number of parts. These parts are so small that they are not a curve but a straight line. We can then find the distance between the two points forming these small divisions. By integrating the length of these individual parts together, we can find out the actual length of the curve.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A continuous curve can be represented as a function, y=f(x). We can get the curve by plotting the points generated by the function in a graph. Consider a curve represented by y=f(x) as shown in the figure.
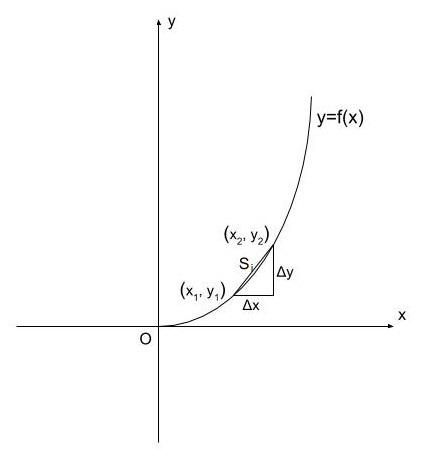
Let us divide the curve into n numbers of equal parts. We can notice that each part gets shorter when we increase the number of divisions.
Let Δx and Δy be the horizontal and vertical components of each division and S be the length of the division.
If (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are the two ends one division, its length will be given by the equation
⇒S1=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2
⇒S1=Δx12+Δy12
Similarly, S2=Δx22+Δy22, S3=Δx32+Δy32 …, Sn=Δxn2+Δyn2.
The total length of the curve will be equal to the summation of all these divisions. Therefore
⇒S≈i=1∑n(Δxi)2+(Δyi)2
where i=1 denotes that the incremental value is equal to one.
The first derivative of the function f′(x) is equal to ΔxΔy since it is equal to the rate of change of the output y with respect to the input x.
Now let us multiply and divide Δyi by Δxi to introduce f′(x)in the equation.
⇒S≈i=1∑nΔxi2+(ΔxiΔxiΔyi)2
⇒S≈i=1∑nΔxi2(1+(ΔxiΔyi)2)
⇒S≈i=1∑nΔxi(1+(ΔxiΔyi)2)
As the number of divisions becomes very large (n→∞lim), the length of the division, S will get closer to zero. Also, the accuracy of our calculation will be increased. The values Δxand Δy will become very small and they are denoted as dx and dy.
⇒S≈i=1∑nΔxi(1+(dxdy)2)
Since f′(x)=dy/dx
⇒S≈i=1∑nΔxi(1+(f′(x))2)
The above summation can be expressed as an integral
⇒S=a∫bΔxi(1+(f′(x))2) ……(1)
Where a and b are the starting and ending points of the curve. Equation (1) can be used to calculate the length of the curve formed by the function y=f(x) with starting and ending points equal to a and b respectively.
Note:
We can also calculate the length of any portion of the given curve using equation (1). By knowing the coordinates of the starting and ending points of the portion of a given curve, we can replace points a and b with those points in equation (1) to find out its length.
