Question
Question: How do you find absolute minimum and maximum in calculus?...
How do you find absolute minimum and maximum in calculus?
Solution
We first explain the concept and then take an example of f(x)=−x3−6x2−9x−2. We equate it with 0. Extremum points in a curve have slope value 0. We solve the quadratic solution to find the coordinates and the points.
Complete step by step answer:
To find the extremum points we need to find the slope of a function and also the value of the point where the slope will be 0. Extremum points in a curve have slope value 0.
The slope of the function can be found from the derivative of the function f′(x)=dxd[f(x)]
We now take an example to understand the concept better. We find the relative extrema of the function f(x)=−x3−6x2−9x−2.
We differentiate both sides of the function f(x)=−x3−6x2−9x−2 with respect to x.
f(x)=−x3−6x2−9x−2⇒f′(x)=dxd[f(x)]=dxd[−x3−6x2−9x−2].
We know that the differentiation form for nth power of x is dxd[xn]=nxn−1.
Therefore, f′(x)=dxd(−x3)+dxd(−6x2)+dxd(−9x)+dxd(−2)=−3x2−12x−9.
To find the x coordinates of the extremum point we take −3x2−12x−9=0.
Solving the given quadratic equation
−3x2−12x−9=0⇒x2+4x+3=0
We know for a general equation of quadratic ax2+bx+c=0, the value of the roots of x will be x=2a−b±b2−4ac.
In the given equation we have x2+4x+3=0. The values of a,b,c is 1,4,3 respectively.
We put the values and get x as x=2×1−4±42−4×1×3=2−4±4=2−4±2=−1,−3.
Therefore, from the value of the x coordinates of the extremum points, we find their y coordinates.
We put values of x=−1,−3 in f(x)=−x3−6x2−9x−2.
For x=−1, the value of y=f(−1)=−(−1)3−6(−1)2−9(−1)−2=2.
For x=−3, the value of y=f(−3)=−(−3)3−6(−3)2−9(−3)−2=−2.
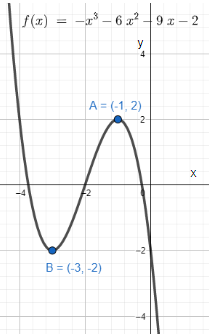
Therefore, the extremum points are (−1,2);(−3,−2).
Note: We also can find which point is maxima and minima by finding f′′(x)=dxd[f′(x)]. If for x=a,b, we find f′′(x) being negative value then the point is maxima and f′′(x) being positive value then the point is minima.
For f′(x)=−3x2−12x−9, we get f′′(x)=−6x−12.
At x=−1, f′′(−1)=−6<0. The point (−1,2) is maxima.
At x=−3, f′′(−3)=6>0. The point (−3,−2) is minima.
