Question
Question: How do you evaluate the definite integral \(\int{\left| x-1 \right|dx}\) from \(\left[ 0,5 \right]\)...
How do you evaluate the definite integral ∫∣x−1∣dx from [0,5] ?
Solution
At first we find out in which interval ∣x−1∣ is negative. We then divide the integral at the point of discontinuity and carry out the integration separately by applying the required formulae of integration.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given definite integral is
0∫5∣x−1∣dx
Let us first analyse the function ∣x−1∣ . We know that,
x-1\to \left\\{ \begin{aligned}
& <0,x<1 \\\
& >0,x>1 \\\
& =0,x=1 \\\
\end{aligned} \right\\}
Thus, we can say that
\left| x-1 \right|=\left\\{ \begin{aligned}
& x-1,x>1 \\\
& -\left( x-1 \right),x<1 \\\
\end{aligned} \right\\}
This means that there exists a discontinuity at x=1 . So, we need to break the integral at x=1 and perform the integrations separately. The integral can be written as,
⇒0∫5∣x−1∣dx=0∫1∣x−1∣dx+1∫5∣x−1∣dx
We have shown earlier that ∣x−1∣ can be written as −(x−1) in the interval [0,1) and as (x−1) in the interval (1,5] . The integral thus becomes,
⇒0∫1∣x−1∣dx+1∫5∣x−1∣dx=0∫1−(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx
Now, we can write 0∫1−(x−1)dx as 1∫0(x−1)dx . Rewriting the integral, we get,
⇒0∫1−(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx....equation1
Let us first integral (x−1) as a definite integral.
∫(x−1)dx=∫xdx−∫1.dx
We know that the integration of ∫xndx=n+1xn+1 . Applying this formula in the above integration, we get,
⇒∫(x−1)dx=1+1x1+1−0+1x0+1
Which gets simplified to
⇒∫(x−1)dx=2x2−x
Applying this integration to equation1 we get,
⇒1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=(2x2−x)10+(2x2−x)15
Which we can evaluate by applying the limits. The integration thus becomes
⇒1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=(0−(212−1))+((252−5)−(212−1))
Further simplification of the expression gives us,
⇒1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=(21)+(215+21)
Performing the additions and subtractions, the integration becomes,
⇒1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=(215+22)
Which finally gives
⇒1∫0(x−1)dx+1∫5(x−1)dx=217
Therefore, we can conclude that the definite integral ∫∣x−1∣dx from [0,5] can be evaluated to 217 .
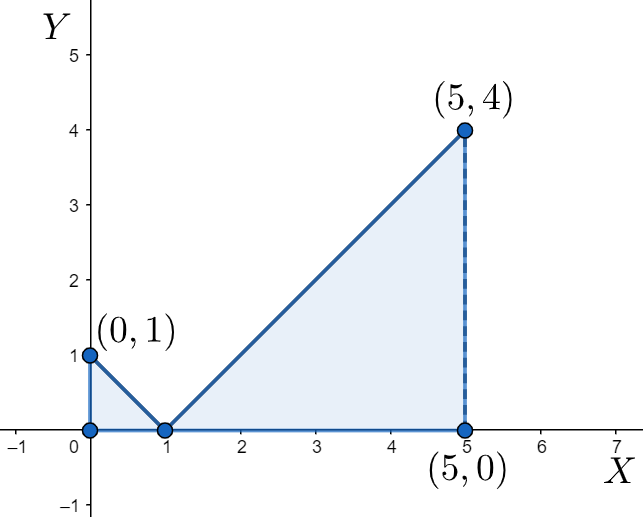
Note: We must remember that the modular function only gives positive outputs. Therefore, we must carefully find out at which point or points the function has zero value and based upon that, we analyse the intervals where the function is positive or negative. We can also solve the problem using the graphical method. We draw the graph of ∣x−1∣ and note the region within which we have to integrate. Here, the area under the graph will be two triangles and thus knowing the important points on the graph, we can easily find out the area under the graph.