Question
Question: How do you evaluate \(\tan \left( {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{2}{3} \right) \right)\) without a cal...
How do you evaluate tan(cos−1(−32)) without a calculator?
Solution
In this question we need to calculate the value of the given expression without using a calculator. We can observe that the given expression consists of two trigonometric identities out of them one is the inverse trigonometric identity. So, we will first consider the inverse trigonometric identity and try to form the triangle using basic trigonometric definitions. After that we will calculate all the sides of the triangle by using Pythagoras theorem and then we can calculate the whatever trigonometric value from the triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that, tan(cos−1(−32)).
Let us assume x=cos−1(−32).
Apply cos function on both sides of the above equation, then we will get
⇒cos(x)=cos(cos−1(−32))⇒cosx=−32
In the above equation we have the value of cosx as negative. So that angle x lies in the second quadrant. We know that the value of tanx will be negative for x in the second quadrant.
We know that the basic definition of the trigonometric ratio cosx will be
⇒cosx=HypotenuseAdjacent side to x⇒32=HypotenuseAdjacent side to x
From the above equation we can assume a triangle as shown in below
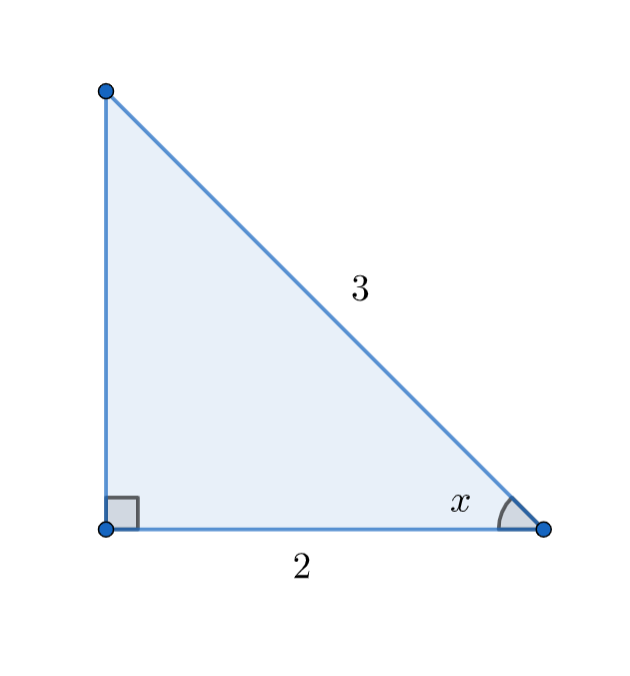
From the Pythagoras theorem, in the above triangle we can write
⇒opposite side2+22=32⇒opposite side2=9−4⇒opposite side=5
Now the triangle will be
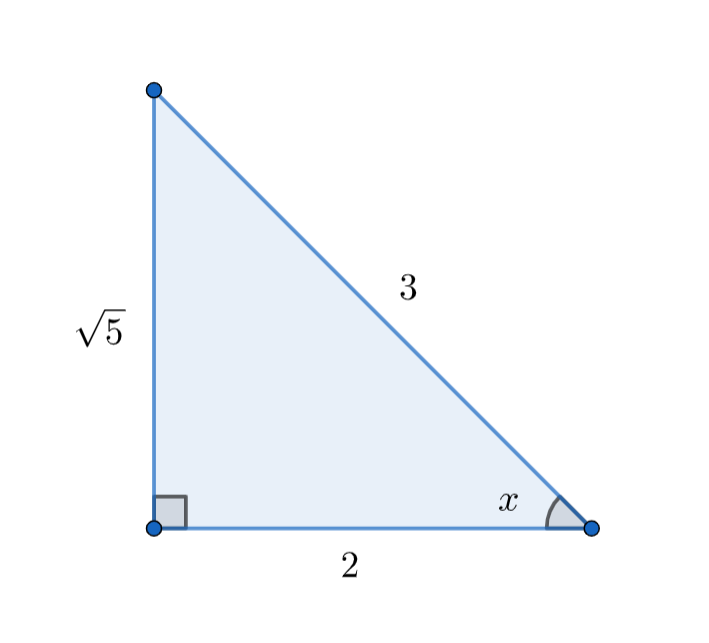
In the above triangle we can write the value of tanx as
⇒tanx=adjacent side to xopposite side to x⇒tanx=25
But the angle x lies in the second quadrant hence the value of tanx will be
⇒tanx=−25
Substituting our assumption x=cos−1(−32) in the above equation, then we will get
⇒tan(cos−1(−32))=−25
Note: For this problem we can also directly calculate the value in another method. After getting the value cosx=−32, we will calculate the value of sinx from the trigonometric identity sin2x+cos2x=1.
⇒sinx=1−cos2x⇒sinx=1−(−32)2⇒sinx=1−94⇒sinx=99−4⇒sinx=35
From this value we can write the value of tanx as
⇒tanx=cosxsinx⇒tanx=−3235⇒tanx=−25
From both the methods we got the same result.
