Question
Question: How do you evaluate \(\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)\) ?...
How do you evaluate sin(211π) ?
Solution
Try to expand sin(211π) and express it in the values that we already know the sin and cos of as, 211π=5π+2π . Then use the trigonometric identity sin(a+b)=sinacosb+sinbcosa to express sin(211π) as sin(5π+2π) . Here, a is 5π and b is 2π .
Complete step by step answer:
This type of question is mainly asked to check whether one remembers the formula sin(a+b)=sinacosb+sinbcosa and the values of sin and cos at 2π and nπ .
We know, sin(nπ) is 0 for all n belonging to integers, sin(2(4n+1)π) is 1 for all n belonging to integers, cos(2(2n+1)π) is 0 for all n belonging to integers and cos((2n+1)π) is -1 for all n belonging to integers.
We know, 211π=210π+π
⇒211π=210π+2π
Since 10 is divisible by 2 and when dividing 10 by 2 we get 5,
⇒210π+2π=5π+2π
Thus, sin(211π)=sin(5π+2π)
Now, taking a as 5π and b as 2π and applying it in the formula of sin(a+b)=sinacosb+sinbcosa we have,
sin(5π+2π)=sin(5π)cos(2π)+cos(5π)sin(2π) .
sin(5π) is of the form sin(nπ) so equal to 0 , sin(2π) is of the form sin(2(4n+1)π) so equal to 1 , cos(5π) is of the form cos((2n+1)π) so equal to -1 and cos(2π) is of the form cos(2(2n+1)π) so equal to 0.
⇒sin(5π)cos(2π)+cos(5π)sin(2π)=0×0+(−1)×(1)
Thus, sin(211π)=−1
Note: One must remember the basic values of sin and cos, it is very common to make mistakes in the signs for +1 and -1 when using the values of sin and cos. Another common mistake is to make sign mistakes in the sin(a+b) formula.
Alternatively, one can directly see that 211π directly is of the form sin(2(4n+3)π) and thus it would be equal to -1.
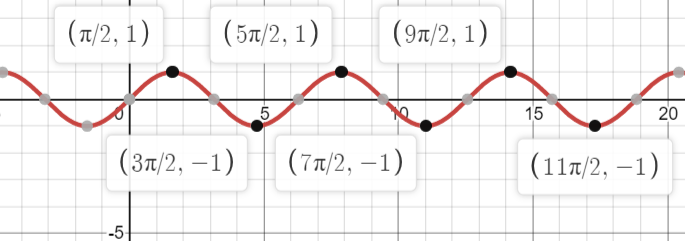
You can also look at the graph and to see the value.