Question
Question: How do you evaluate \(\cot \left( \arctan \left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right) \right)\)?...
How do you evaluate cot(arctan(53))?
Solution
We explain the function arctan(x). We express the inverse function of tan in the form of arctan(x)=tan−1x. We draw the graph of arctan(x) and the line x=53 to find the intersection point. Thereafter we take the cot ratio of that angle to find the solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The given expression is the inverse function of trigonometric ratio tan.
The arcus function represents the angle which on ratio tan gives the value.
So, arctan(x)=tan−1x. If arctan(x)=α then we can say tanα=x.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of 2π.
The general solution for that value where tanα=x will be nπ+α,n∈Z.
But for arctan(x), we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio tan we have −2π≤arctan(x)≤2π.
The graph of the function is
We now place the value of x=53 in the function of arctan(x).
Let the angle be θ for which arctan(53)=θ. This gives tanθ=53.
For this we take the line of x=53 and see the intersection of the line with the graph arctan(x).
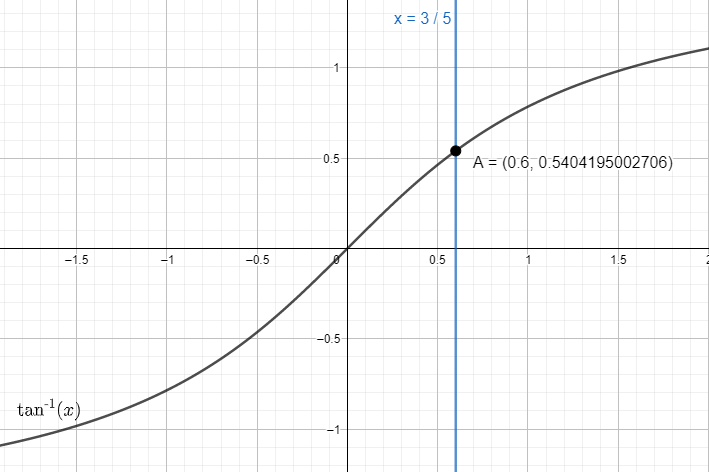
Putting the value in the graph of arctan(x), we get θ=30.96. (approx.)
We get the value of y coordinates as 30.96∘.
Now we take cot(arctan(53))=cot(30.96∘)=35.
Therefore, the value of cot(arctan(53)) is 35.
Note: We can also apply the trigonometric identity where cotθ=tanθ1. Also, in the exact solution domain of −2π≤θ≤2π, tan(tan−1x)=x.using those identities we get
cot(arctan(53))=tan(tan−1(53))1=531=35.
