Question
Question: How do you derive the law of cosines?...
How do you derive the law of cosines?
Solution
This problem deals with the derivation of the law of cosines. The law of cosines is for calculating one side of a triangle when the angle is opposite and the other two sides which are known. Here let the unknown side be c, and the angle opposite angle to this side is α, and the other two sides are a and b, from here we can derive the law of cosines.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using the notations as given in the above hint, the law of cosines states where α denotes the angle contained between sides of lengths a and b and the opposite side of length c.
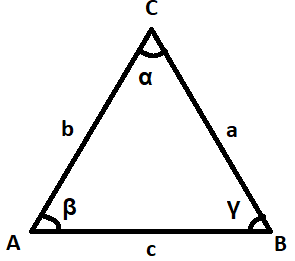
Then the law of cosines is given by:
⇒c2=a2+b2−2abcosα
Here a,b and c are the sides of the triangle and αis the angle between the sides band c.
This can be applied to any triangle.
If the unknown side is a and the angle opposite to this side is the angle is β, where the other two sides are known b and c. Then using the law of cosines, the side a is given by:
⇒a2=b2+c2−2bccosβ
If the unknown side is b and the angle opposite to this side is the angle is γ, where the other two sides are known a and c. Then using the law of cosines, the side b is given by:
⇒b2=a2+c2−2accosγ
Note: Please note that the law of cosines is used here to find the unknown side of a triangle, this can be used to find the unknown angle which is given by:
⇒cosα=2aba2+b2−c2
Law of sines is used to find all the sides of the triangle and all the angles of the triangle, given by:
⇒sinβa=sinγb=sinαc
