Question
Question: How do you convert the following: Ethyl alcohol to ethoxy ethane. Acetone to 2-methyl-2-propanol...
How do you convert the following:
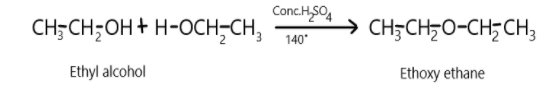
Ethyl alcohol to ethoxy ethane.
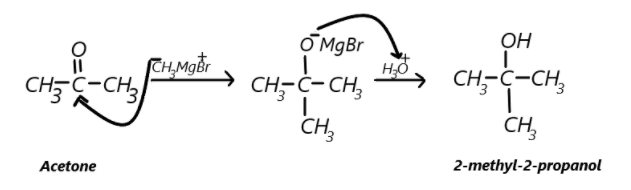
Acetone to 2-methyl-2-propanol.
Solution
Ethers are prepared by the intermolecular dehydration of alcohols following the SN2 mechanism. We know that carbonyl carbons are generally converted to alcohols using Grignard reagent.
Complete Step by step answer: In the first conversion we need to know the dehydration of alcohols in the presence of protic acids at 140∘Cwill result in the formation of ether and it is a nucleophilic bimolecular reaction. so when ethyl alcohol will react with concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature of 140∘C, it will result in the formation of ethoxy ethane which is our desired product and liberation of water molecules. This can be depicted as:
In the second compound we are to convert acetone which has a ketonic group thus a carbonyl carbon and we have to convert this carbonyl compound to alcohol, this can be done by using Grignard reagent which has a general formula R−MgXwhich will ionise as the alkyl part has a negative charge which will attack the carbonyl carbon. Here we can take CH3−MgBras Grignard reagent, so methyl will attack the carbonyl carbon and electrons from double bond will shift to oxygen and the product will have a MgBrattached to the oxygen, now if the hydrolysis take place in the presence of H3O+ so hydrogen will be added in place of MgBrto the oxygen finally forming the desired product which is 2-methyl-2-propanol. This can be represented as:
Note: Ethoxy ethane can also be prepared using Williamson’s synthesis which is an easy and important method to prepare all types of ethers, in this method alkyl halide is allowed to react with sodium alkoxide and again it is a nucleophile substitution reaction which undergoes via SN2.
