Question
Question: How do you calculate \[\arcsin \left( { - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)\]?...
How do you calculate arcsin(−23)?
Solution
We use the concept that arc means inverse of the function. We are given the value of sine of an angle. Use the trigonometric identity sin2x+cos2x=1 to find the value of cosine of the same angle. Divide sine of the angle by cosine of the angle to calculate tangent of the angle. Use a quadrant diagram to write the value of angle for cosine.
- Arc sine of a function is defined as the inverse sine of the function. When siny=x, then we can write arcsinx=sin−1x=y.
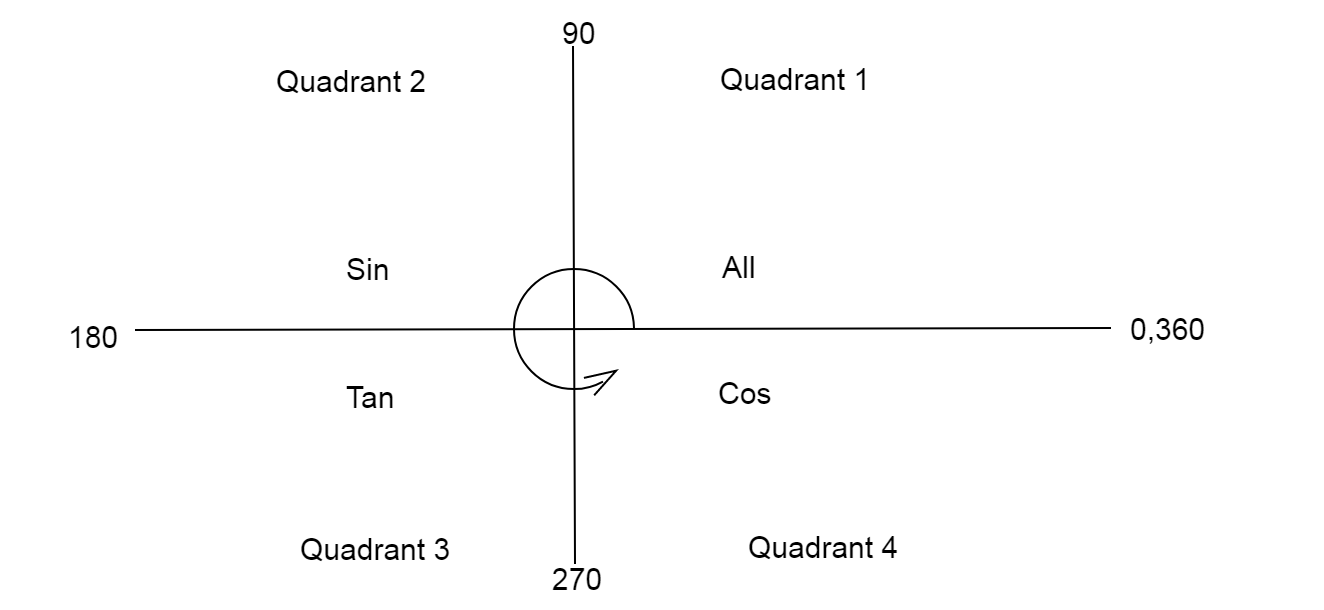
- We know the values of all trigonometric angles are positive in the first quadrant.
Values of only sinθ are positive in the second quadrant.
Values of only tanθ are positive in the third quadrant.
Values of only cosθ are positive in the fourth quadrant.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume the angle as ‘x’
We are given that arcsin(−23)
Since we know that arcsinx=sin−1x=y
Then we can write arcsin(−23)=sin−1(−23)=y
⇒sin−1(−23)=y
Take sine on both sides of the equation
⇒sin[sin−1(−23)]=siny
Cancel sine and sine inverse on left side of the equation
⇒−23=siny … (1)
We know that the value of sin3π=23
Also, we know sine is an odd function, so, sin(−x)=−sinx and that sine function is negative in the third and fourth quadrant.
⇒−(23)=siny
⇒−(sin3π)=siny
And we can write using the concept of odd function
⇒sin(−3π)=siny
Take inverse sine function on both sides
⇒sin−1[sin(−3π)]=sin−1[siny]
Cancel inverse function by the function
⇒y=−3π
∴The values of arcsin(−23) is −3π
Note: Many students make the mistake of calculating the angle inside sine as positive which is wrong, the value of sine is given negative so we will have to look at the quadrant diagram and figure out what is the sign of the angle. Keep in mind we can use table for trigonometric terms if we don’t remember the values at some common angles0∘,30∘,45∘,60∘,90∘
| ANGLEFUNCTION | 0∘ | 30∘ | 45∘ | 60∘ | 90∘ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sin | 0 | 21 | 21 | 23 | 1 |
| Cos | 1 | 23 | 21 | 21 | 0 |
| Tan | 0 | 31 | 1 | 3 | Not defined |
