Question
Question: How do I use linear programming in excel 2010?...
How do I use linear programming in excel 2010?
Solution
Solver Add-in is used for solving linear programming problems in Excel 2010.The Solver Add-in is one of the Microsoft Office Excel add-ins a supplemental program that adds custom commands or custom features to Microsoft Office. You need to check the availability of this add-in and if not available install it. To use it in Excel, load this add-in as mentioned as follows: First open the Microsoft excel then Click on the image of Microsoft Office Button, and then click Excel Options, which is on the bottom bar. There you will find Add-Ins. Click on Add-Ins, and then in the Manage box, select Excel Add-ins (at the bottom) and Click Go. In the Add-Ins available box, select the Solver Add-in check box, and then click OK. If Solver Add-in is not listed in the Add-Ins available box, click Browse to locate the add-in. If you get prompted that the Solver Add-in is not currently installed on your computer, click Yes to install it. After you load the Solver Add-in, the Solver command is available in the Analysis group on the Data tab. For solving linear programming problems.
Complete step-by-step answer:
1. Open a new Excel Worksheet by clicking the window button on the taskbar, then All Programs, clicking on Microsoft Office, and selecting Microsoft Excel 2010.
2. First verify that the solver Add-In is enabled or not. For this click on Data in the menu across the top of the window. On the extreme right you will find the Solver. If you don’t find it then install it.
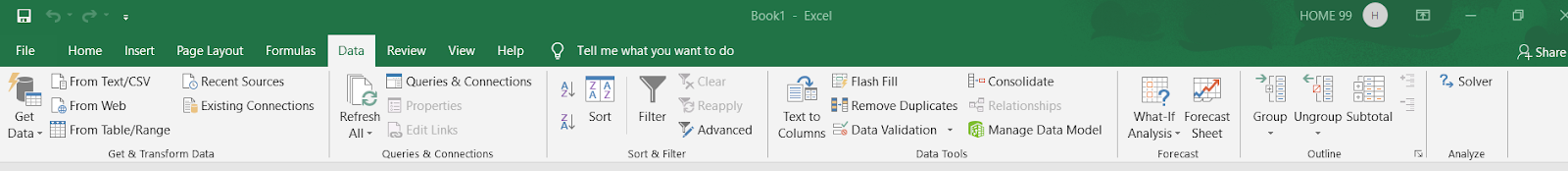
3. For Installing Solver Add-In click on File in the top left corner of the window. Select Options. In the next window, select Add- Ins from the list on the left side. At the bottom, click on go.
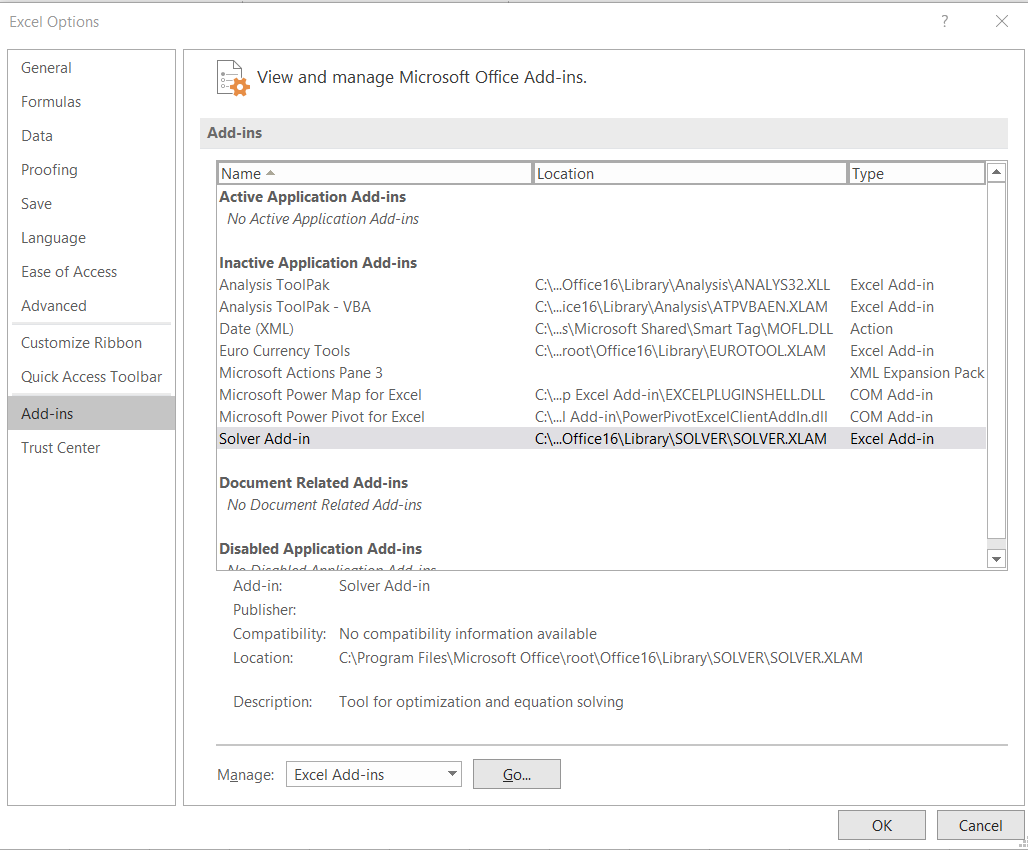
4. After this in the Add-Ins window, select "Solver Add-in". Click OK
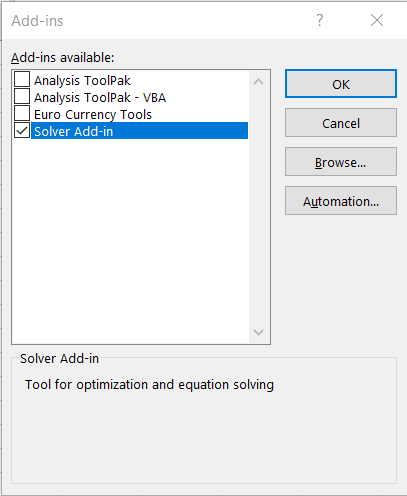
5. To confirm this, go back to Data again and look for Solver Add-In in the extreme right of the taskbar.
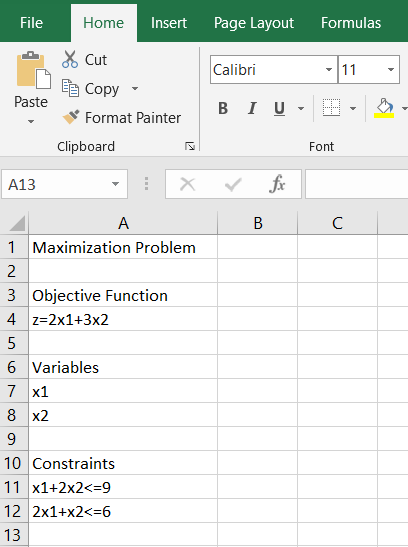
6. Here’s an elaborative example of solving Linear programming problems in excel 2010. Consider the problem: Maximize z=2x1+3x2 Subject to x1+2x2≤9, 2x1+x2≤6, x1≥0and x2≥0.
7. Microsoft Excel makes it convenient to solve a “Maximization Problem” or “Minimization Problem.” The following steps are used to solve the above maximization problem. Minimization problems are also done the same way except for some slight differences
8. Column A is only used for displaying the parts of the problem and labeling the objective function, variables, and constraints whereas Column B is used to solve the problem, so formulas will only be typed in Column B.
9. Click on cell A1 and type the label: “Maximization Problem” or “Minimization Problem'' depending on the problem you are solving for. Press Enter after each entry. Stretch Columns A and B to be wider by putting the cursor in between the column headers until the cursor changes to “+” and then dragging the cursor to the desired width.
10. Use the down arrow key to move to cell A3 and type the label: “Objective Function”.
11. Click on cell A4 and type the objective function: z=2x1+3x2
12. Click on cell A6 and type the label: “Variables”
13. Using the down arrow key, click on cell A7 and type the first variable, x1
14. Using the down arrow key, click on cell A8 and type the second variable, x2. If there are more variables, type each variable on the following rows.
15. Skip a row using the down arrow key and type the label: “Constraints”.
16. Type each constraint inequality in a separate row of Column A. Leave out the basic restrictions of and because these constraints can be set automatically in the Solver process.
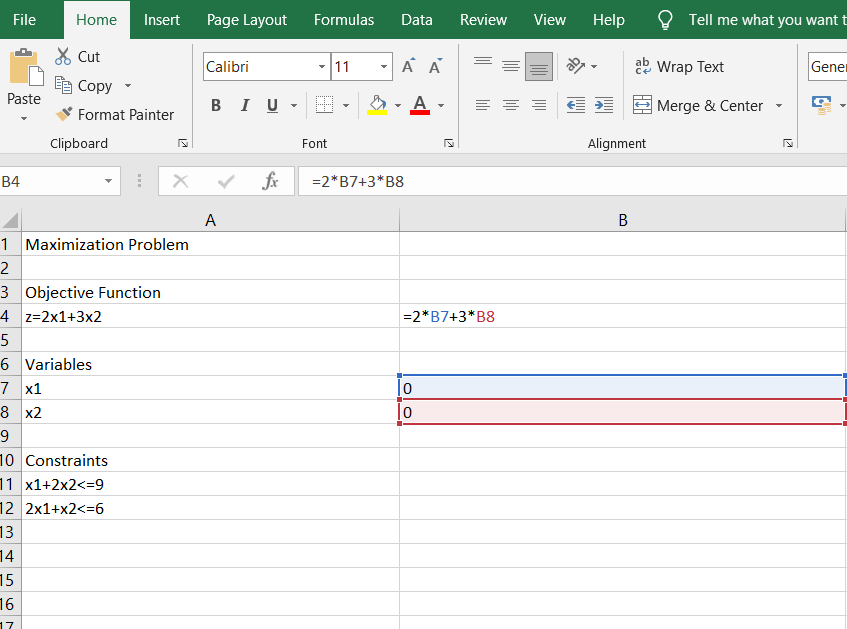
17. Now type the equations in Column B using cell names in the formulas instead of variable names. Click on cell B4 and type the objective function. The objective function z=2x1+3x2should be typed as “=4x∗B7+5∗B8”. Notice variable x1 was replaced with its cell location B7. Variable x2 was replaced with its location of B8. Repeat for all the variables. After you enter each formula, you will see a zero on your Excel worksheet. For the solver to work, you must use the cell names in Column B instead of the variables.
18. In Column B, use the down arrow to get to the variable rows and type zeros in cells B7 and B8. If you have more variables, continue entering zeros. Below is a screen print with formulas shown. Note: To show formulas, depress “”and “`Ctrl” buttons at the same time; to change back, depress “” and “Ctrl” buttons again.
19. In Column B use the down arrow to get to the constraint’s rows. Type the following formulas, replacing the variables with the cell names:
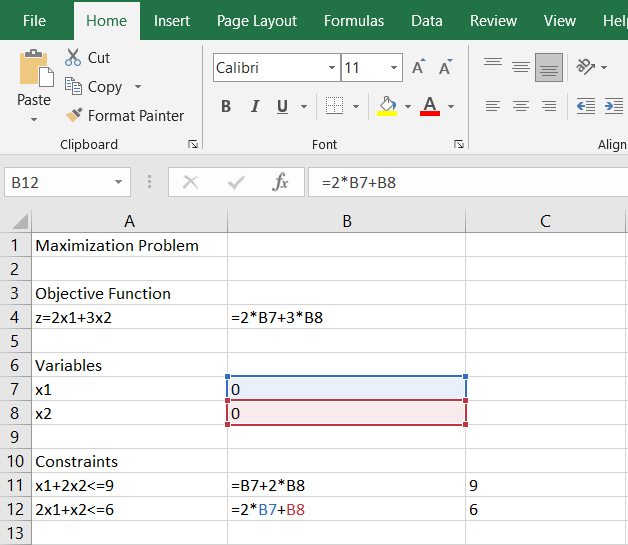
In cell B11, constraint x1+2x2 should be typed as “=B7+2∗B8”
In cell B12, constraint 2x1+x2 should be typed as “=2∗B7+B8”
Notice that the values will show as zeros on the worksheet.
20. In Column C, type the augments (constants on the right side of the constraint inequalities) for each of the constraints. In cell C10, type "Augments". In cell C11, type "9"and in cell C12 type "6".
21. Click in cell B4 (the objective function) before going to the Data menu and selecting “Solver.” The Solver Parameters window will open.
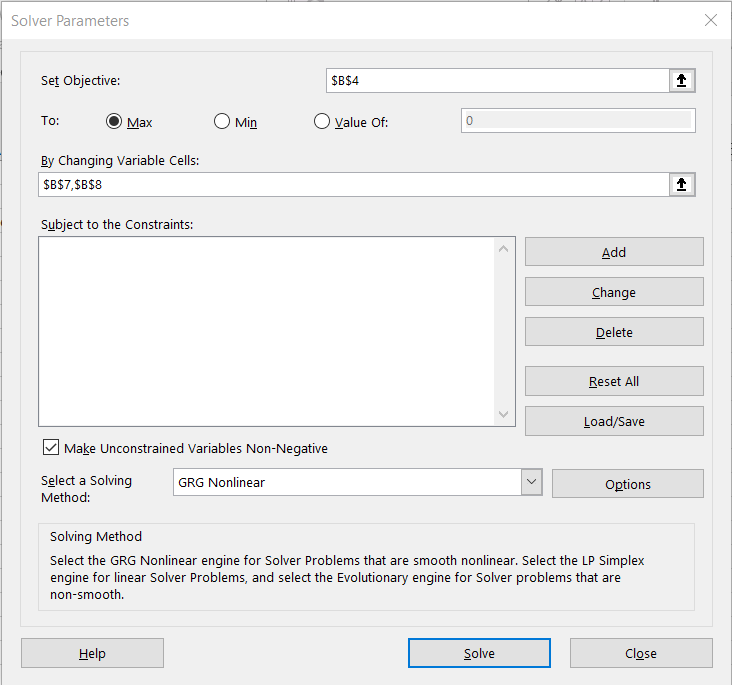
Make sure the Set Objective box is set to “B4” (If not, close the window, click in cell B4, and open the Data Solver option again.) Note: "Objective" refers to the cell location of the objective function formula. On the top: line select “Max” to find the maximum value or select “Min” to find the minimum value. Click in the By Changing Variable Cells: box and type variables “B7, B8” separated by commas. If you have more than two variables, make sure you include them in the list. Click in the Subject to the Constraints box and then click the Add button. The Add Constraint window will pop up.
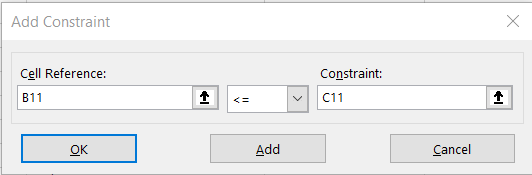
Type the first constraint cell location. For example, enter "B11" in the Cell Reference box. Select the appropriate sign from “<=”, “=”, or “>=” as it appears in the linear programming problem by clicking on the down arrow in the middle box. In the Constraint box, enter the first augment cell location of "C11". Click the Add button. Enter the rest of the constraints and augments in the same manner. When completed, click OK. See below.
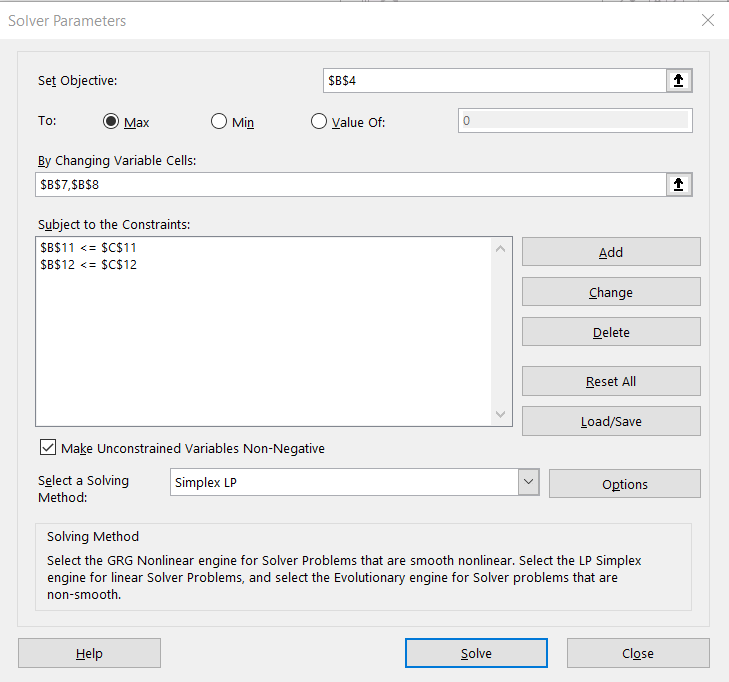
22. In the Solver Parameters window, click on "Make Unconstrained Variables Non-Negative" In the box for Select a Solving Method: choose "Simplex LP".
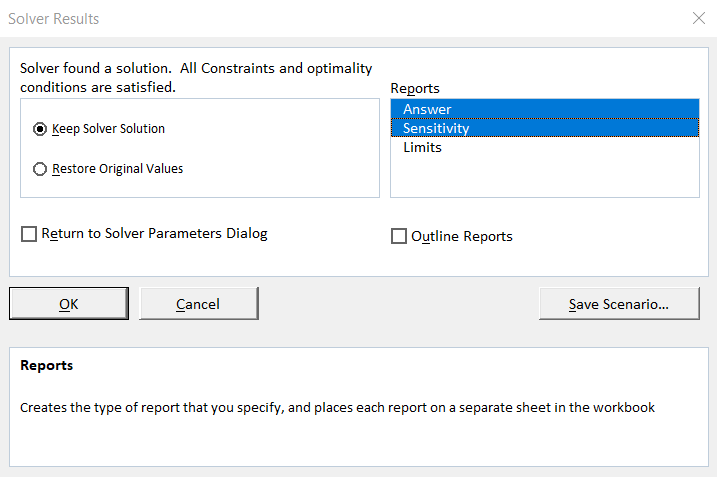
23. In the Solver Parameters window click the Solve button.
24. A Solver Results window will appear telling you that the solver found a solution. Click beside "Keep Solver Solution". Select Answer and Sensitivity from the Reports box and then click OK.
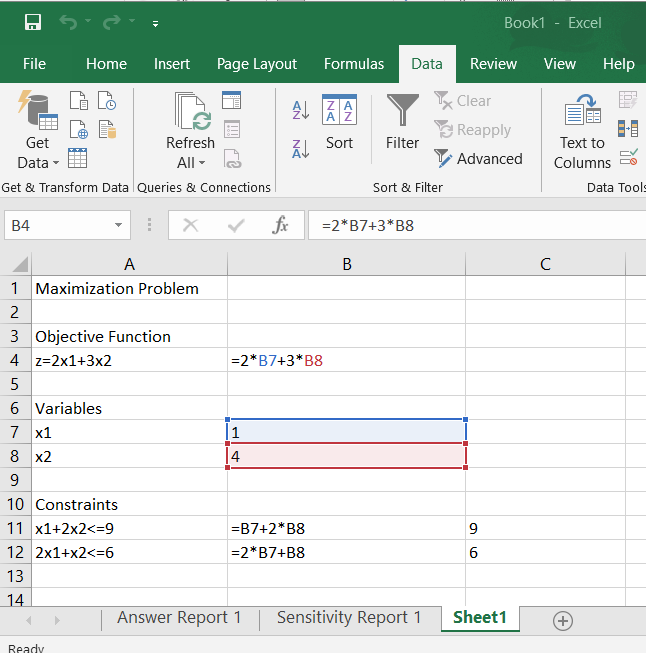
Finally, the Excel worksheet should look like the screen print on the next page.
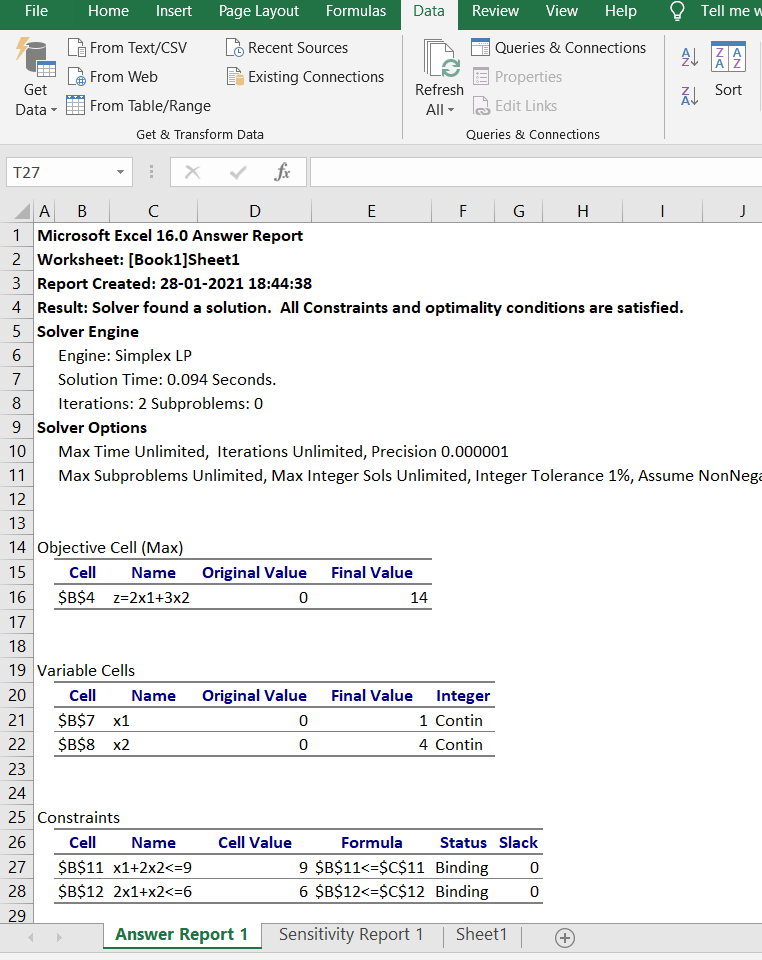
25. A sheet tab labeled “Answer Report 1” should now be at the bottom of the screen. Click on it to see the results.
26. If you need to re-run the Solver, type zeros in the cells for the variables. Also, right-click on the tabs displaying the results (Answer Report, Sensitivity Report), and delete each of them.
27. Interpret the results. In this sample problem, the maximum occurs when x1=1and x2=4.
Note: You do not type the quotation marks. The quotation marks indicate exactly what is to be typed while mentioning the variables in solver. Do not type the absolute signs (dollar signs) because Excel will add them in for you.
