Question
Question: How can you tell the difference between an ester, ketone, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, amines, amides ...
How can you tell the difference between an ester, ketone, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, amines, amides and phenol using infrared spectroscopy?
Solution
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is the analysis of infrared light interacting with a molecule. This can be analysed in three ways by measuring absorption, emission and reflection. The main use of this technique is in organic and inorganic chemistry.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first draw the structure of functional groups.
Ester:
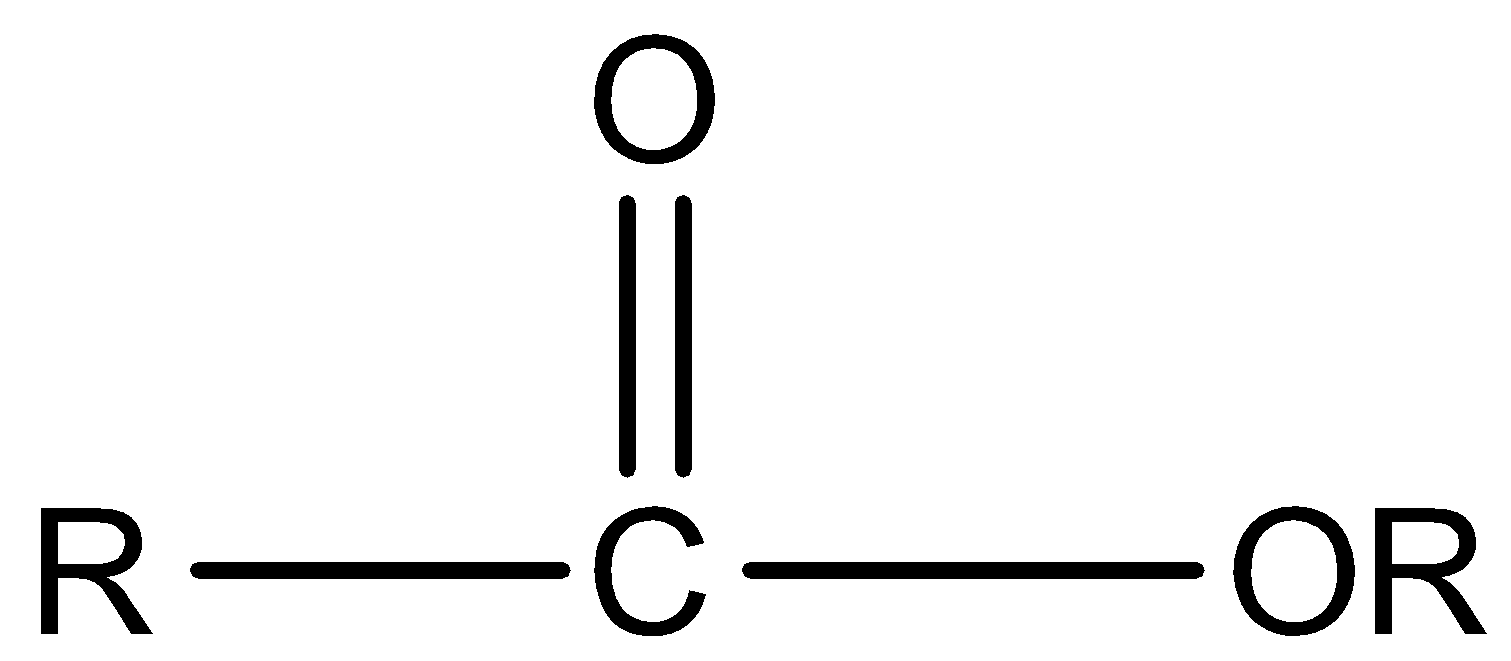
Ketone:
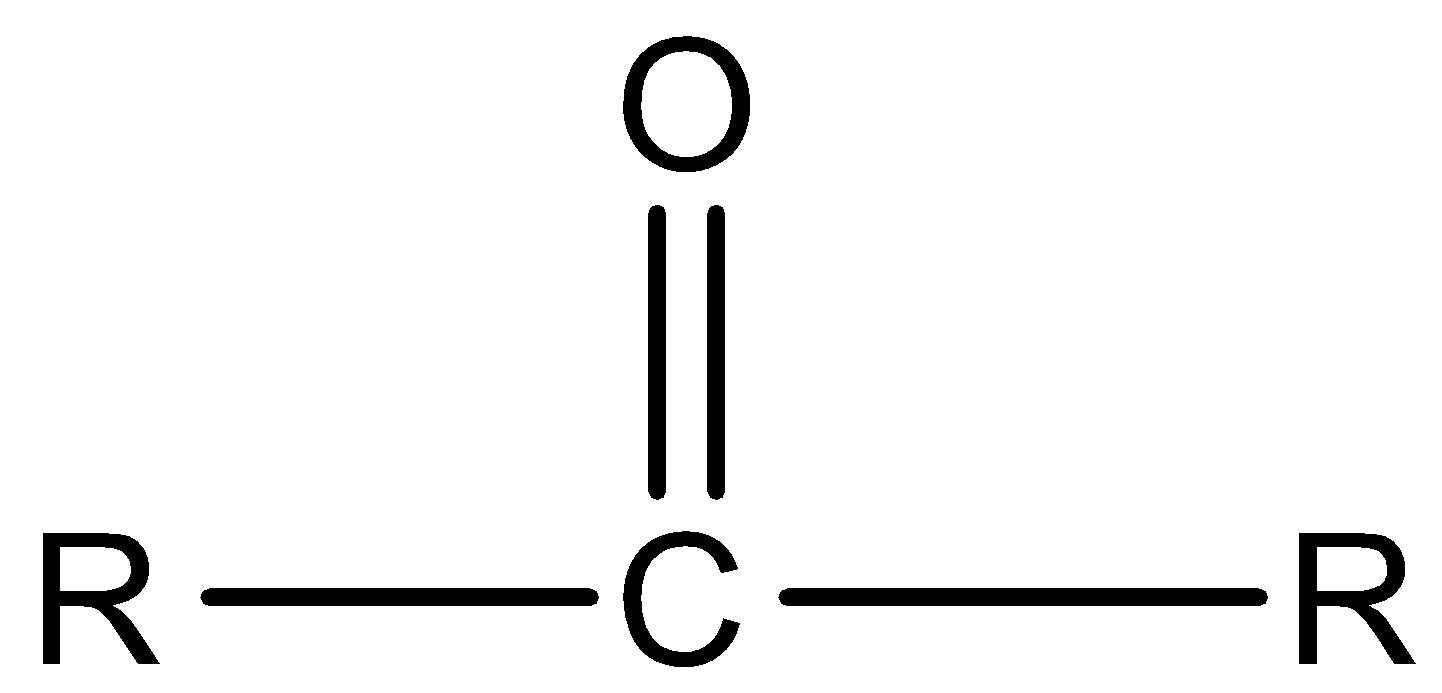
Carboxylic acid
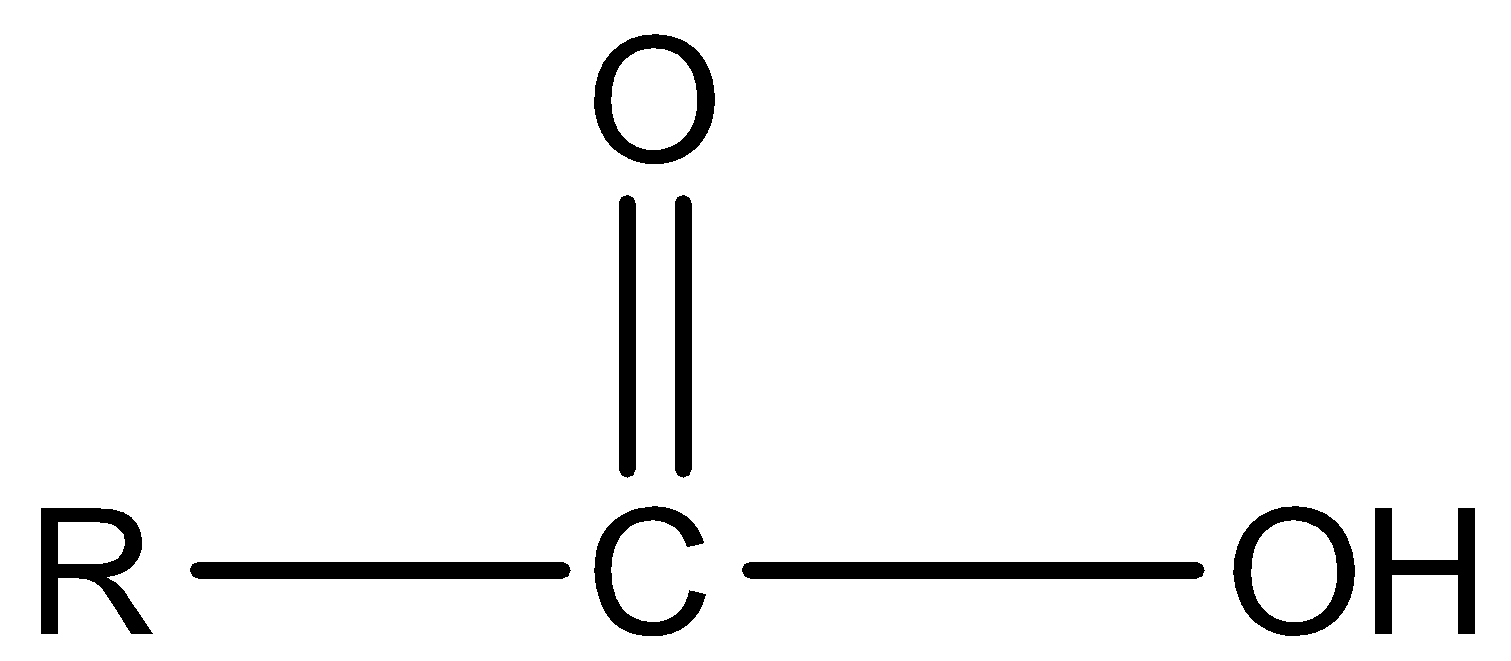
Aldehyde
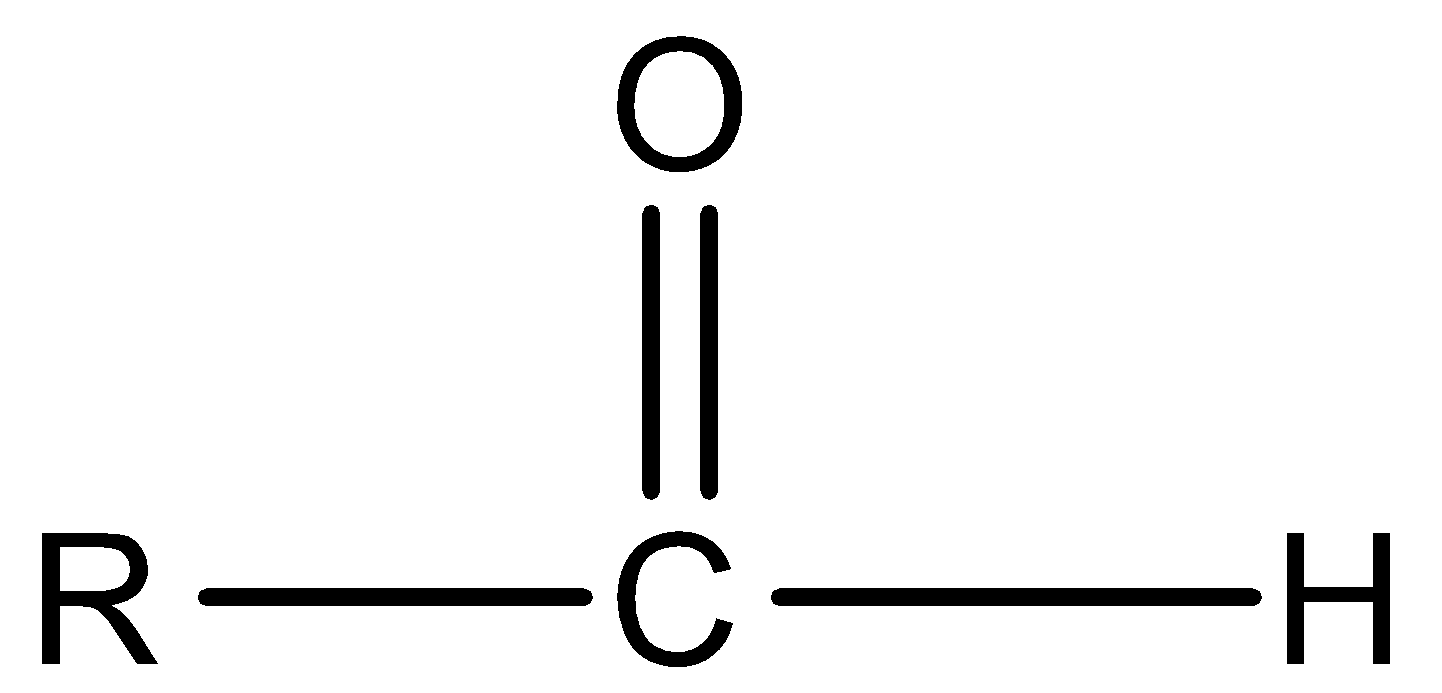
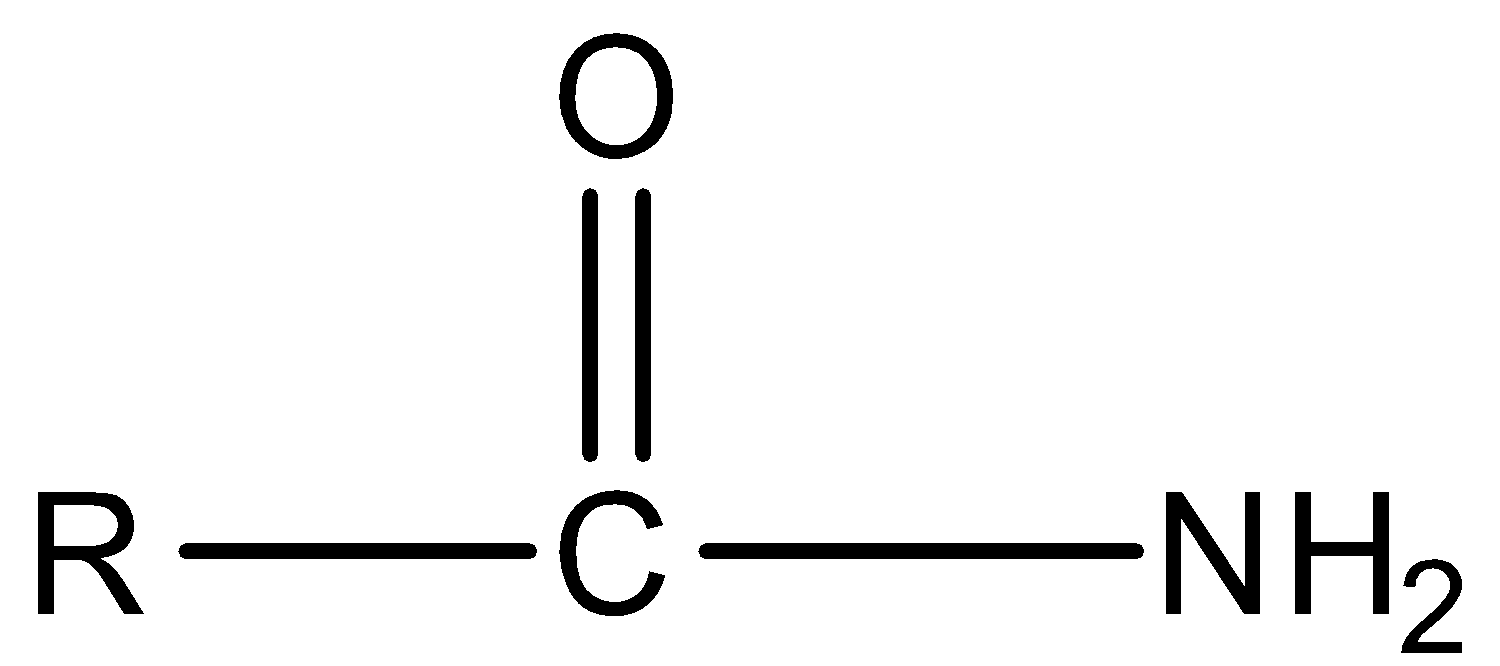
Amide
The differences between the functional groups are as follows:
| Aldehyde | ketone| Carboxylic acid| Ester| Amide| Anhydride| Acid chloride
---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---
Structure| R-CHO| R-CO-R| R-COOH| R-COOR| RCONH2| RC2O3R| R-COCl
Stretching frequency| 1740-1720 Hz| 1725-1705 Hz| 1725-1700 Hz| 1750-1730 Hz| 1680-1630 Hz| 180 and 1760 Hz| 1800 Hz
Additional Information:
The distinction among the frequency range of an acid vs an ester is a thrilling one, as at the surface of it they may be electronically pretty similar (in both cases the carbonyl is subsequent to an electronegative oxygen).
Keep in mind that the stretching frequency will increase with bond power. Therefore using your statistics we will say that the ester is more potent than the ketone while the acid is weaker.
IR spectroscopy simply identifies the carbonyl group C=O of organic compounds: of amides, or esters, or ketones, of acids as a sturdy sharp absorption. The problem is while they occur as a strong absorption.
Phenols and amines of direction do now not comprise the carbonyl absorption. Sometimes, the O-H or N-H bonds may be inferred on the IR spectrum. Anyway, IR spectroscopy will provide you with an idea of the functional group; they will not discover the molecule.
Note: It is to be noted that An ester is a ketone wherein one of the carbons is bonded to an oxygen that is bonded to something else. A carboxylic acid is in which an ester's oxygen is bonded with hydrogen. Aldehyde is a ketone wherein one of the bonds at the carbon is hydrogen.
