Question
Question: How can we convert \( R-3-methylhexane-3-ol \) to Fischer projection?...
How can we convert R−3−methylhexane−3−ol to Fischer projection?
Solution
Hint : Fischer projection is defined as the two dimensional representation of the three dimensional molecule of the organic compound with help of the projection. They help in representing the monosaccharides in biochemistry and organic chemistry. It helps in depicting the stereo formula in two dimensional forms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So to know how the Fischer projection of a compound is formed let us take the example of R−3−methylhexane−3−ol . In making the Fischer projection we should firstly draw the chain vertically and place the aldehyde group at the top. The bonds present above and below any of the two adjacent carbon atoms are present behind the plane of paper.
Whereas the horizontal bonds are coming out of paper. As we know that the geometry of carbon is tetrahedral that means the vertical groups one and four should be present behind the paper. When we have a longer vertical chain we look at any two of the adjacent atoms. The steps for conversion are:
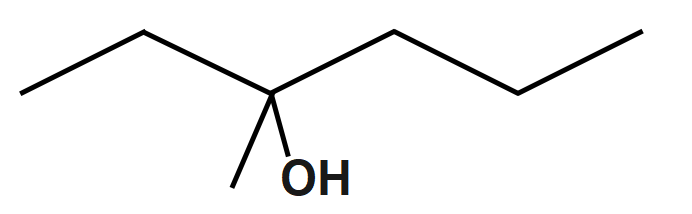
Step1: Draw the bond-line structure of R−3−methylhexane−3−ol and then convert this to a wedge-dash structure. Start by making the CH bond a wedge and the OH bond a dash. We have a
50 chance of getting it right.
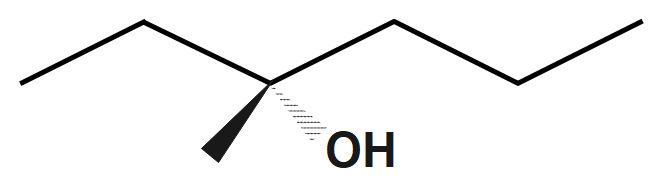
Step 2. Draw the skeleton Fischer projection
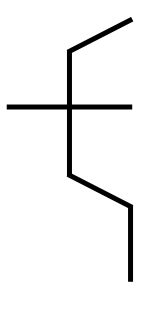
Step3: To convert this to a Fischer projection, draw a vertical line of six carbon atoms, with a cross at C−3 Attach the CH and the OH groups to the correct sides.
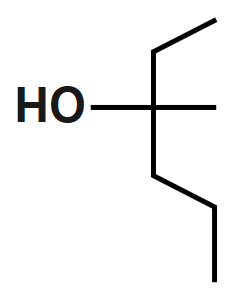
Note :
A dextrorotatory compound is prefixed with (+) or d. whereas the levorotatory compound is prefixed with the (−) or l. These lowercase are considered to be different from those of the D and L prefixes which are used in differentiating chiral configurations with the organic compounds. The carbohydrate is a biomolecule which comprises the carbon, hydrogen and the oxygen atoms.
