Question
Question: How can I draw the structures of four isomers of amides for the formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\...
How can I draw the structures of four isomers of amides for the formula C5H11NO ?
Solution
The molecules having the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms are known as isomers. We should know the structure of the amide functional group. By substituting the number of atoms used in amide from the given molecular formula we will determine the hydrocarbon skeleton. Then we will draw the possible structures of hydrocarbon skeleton and will attach the amide functional group.
Complete step-by-step answer: The −CONH2is known as amide function group. The structure of amide functional group is shown as follows:
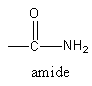
The given molecule formula of amide is C5H11NO. In which one carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and two hydrogenates are constituting a functional group. So, the remaining carbon and hydrogen atoms are forming the hydrocarbon skeleton. The remaining hydrocarbon skeleton is C4H9.
We have drawn this hydrocarbon skeleton exploring the possibilities and we have to attach the amide functional group to get the four isomers of amide.
We can draw an isomers having four carbon in a chain as follows:
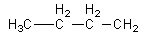
We will attach the amide functional group with −CH2 to get an isomer.
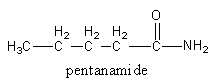
So, the first isomer of the amide is pentamide.
We can draw an isomers having three carbon in a chain and fourth carbon as a methyl substituent as follows:
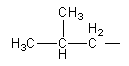
We will attach the amide functional group with −CH2 to get an isomer.
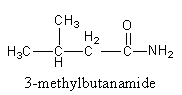
So, the second isomer of the amide is 3−methylbutanamide.
In the above isomer we attached the methyl group to third position from the amide functional group. We can also attach the methyl group at second carbon from the amide functional group.
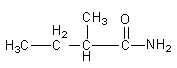
So, the third isomer of the amide is 2−methylbutanamide.
We can also draw an isomer having three methyl group at second carbon.
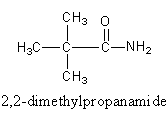
So, the fourth isomer of the amide is 2,2−dimethylpropanamide. Which is also known as pivalamide.
Therefore, the four isomers of amide are pentanamide, 2−methylbutanamide, 3−methylbutanamide, and 2,2−dimethylpropanamide.
Note: Isomers have the same molecular formula but different chemical formula. A molecular formula shows the total number of an atom in the compound. The chemical formula shows the different groups of atoms of a molecule. To draw the structure of the isomers from the given molecular formula first we determine the degree of unsaturation by using the following formula:
D.U = C+1−2no. of monovalent−no. oftrivalent
Degree of unsaturation tells the number of unsaturated bonds or number of rings. One degree of unsaturation tells the presence of one ring or one double bond.
