Question
Question: How can atoms achieve stable electron configurations?...
How can atoms achieve stable electron configurations?
Solution
We should know about the valence electrons, octet rule, and covalent bond, electronic configuration, etc. The arrangement of electrons generates the electronic configuration of atoms. The atoms combine to form molecules and then compounds. For the formation of the molecule, the atoms share their valence electrons and form bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
- The atoms have protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the outermost shell. Neutral atoms have a fixed electronic configuration in which the outermost orbitals can be partial-filled, fully-filled, or can have one, or any number of electrons. It depends upon the atomic number of those atoms.
- The fully-filled electronic configurations are more stable. The atoms having eight valence electrons in the outermost shell are stable.
- In the periodic table, the noble gases have a fully-filled electronic configuration. Fully-filled electronic configurations are stable, so every atom tends to achieve the fully-filled configuration. For this, atoms lose or gain electrons.
- For example, consider the formation of ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen. The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s2 and the electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22s3. If somehow hydrogen gets one electron. It can complete its octet. Similarly, nitrogen requires three electrons to complete its octet.
So, nitrogen and three hydrogens will share one-one electrons and nitrogen will form three covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms.
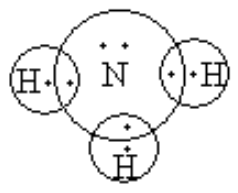
Nitrogen shares three electrons with three hydrogens, so it gets three electrons each form three hydrogen so, it octet gets completed and each hydrogen also gets one electron from nitrogen, so octet so hydrogen also gets completed.
Therefore, by sharing valence electrons, atoms achieve a stable electronic configuration.
Note: According to the octet rule, the atom has eight electrons in the valence shell that are stable but the octet of hydrogen gets completed by two electrons only. The bond formed by the sharing of electrons is known as a covalent bond. The number of electrons shared by an atom depends upon the number of electrons required to complete the octet of that atom. An atom can also accept or donate electrons to achieve a stable octet. The bond formed by the donation and acceptance of electrons is known as an ionic bond.
