Question
Question: How are the TCA and ETC related?...
How are the TCA and ETC related?
Solution
Cell respiration is a three-stage process, through which living cells break down organic fuel molecules in the presence of oxygen for harvesting the energy they require to divide and grow. TCA is tricarboxylic acid and ETC is electron transport chain. TCA cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration, with the first stage being glycolysis. It is also known as citric acid cycle and Krebs cycle. ETC is the last stage in cellular respiration.
Complete answer
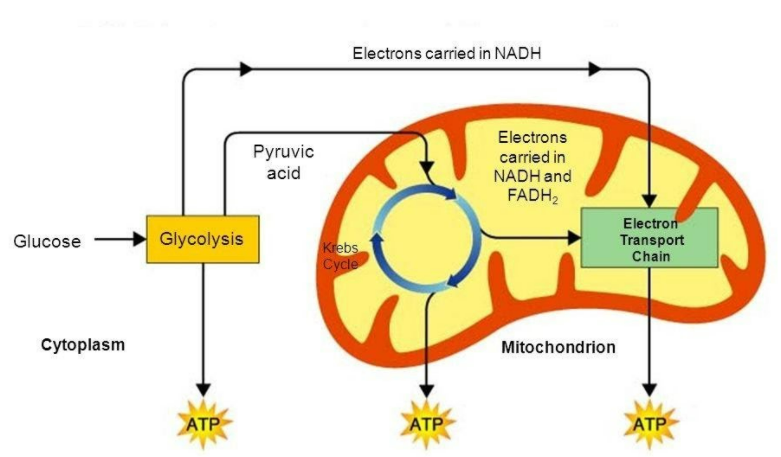
Figure: Relation between TCA cycle and ETC – A diagrammatic representation
In a series of enzymatic reactions, TCA cycle generates the reducing equivalents FADH2and NADH2, that are needed to transfer electrons to the mitochondrial respiratory chain, which is otherwise known as the ETC. As the electrons are funnelled through the complexes present in the inner mitochondrial membrane, a functional ETC generates a mitochondrial membrane potential, which is used to produce ATP. This process needs the presence of oxygen and is known as oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Mitochondrial complex I and II in the ETC replenish NAD+ and FAD respectively, permitting the oxidative TCA cycle to function. Succinate dehydrogenase is the only enzyme, which participates in both the ETC and TCA cycle.
TCA cycle is the major energy-yielding metabolic pathway in cells, providing the larger part of the reduced coenzymes, which will be oxidized by the ETC to yield Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). Coenzymes like NAD+ and FAD are reduced in the TCA cycle, which transfers electrons by ETC with oxygen as the final acceptor. Three NADH2 and one FADH2are generated in one TCA cycle, on entering ETC, yields ten ATP. These ten ATP include one ATP produced by succinate thiokinase at the substrate level.
Note:
Both TCA and ETC occur in the specialized protein complexes present in the inner membrane of mitochondria of eukaryotic organisms and in the inner part of the membrane of the cell of prokaryotic organisms. The TCA cycle gives greater amounts of energy in aerobic conditions through donation of electrons to ETC, creating a proton gradient required for driving ATP synthesis.
