Question
Question: Here, \(\text{1-4 dichlorohexane (1 mole) + NaI (1 mole)}\xrightarrow{Acetone}\) Product of the reac...
Here, 1-4 dichlorohexane (1 mole) + NaI (1 mole)Acetone Product of the reaction is:
(a)
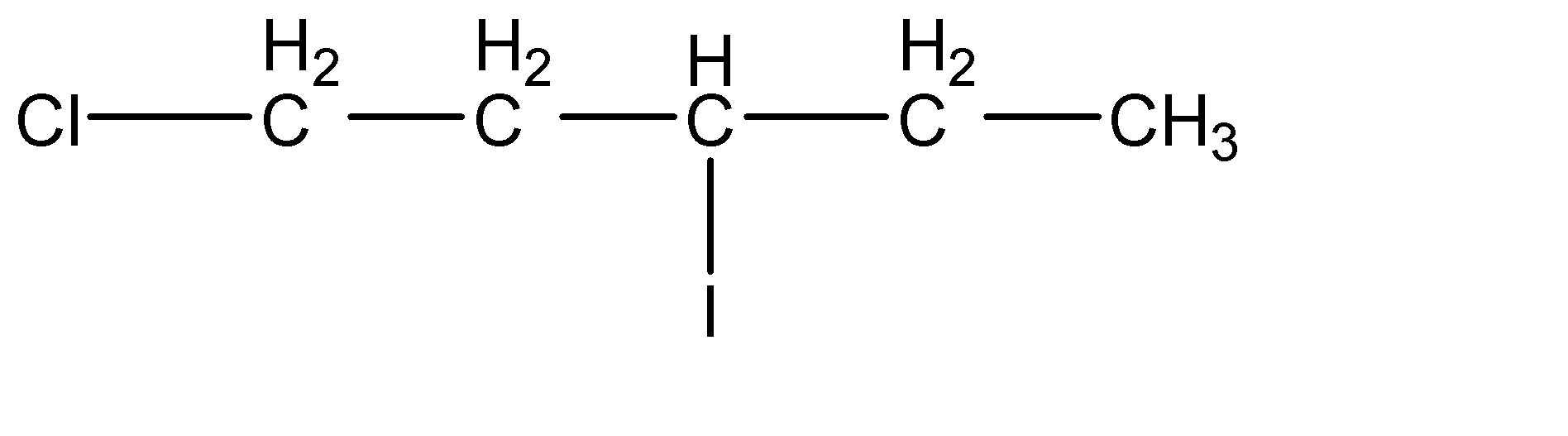
(b)
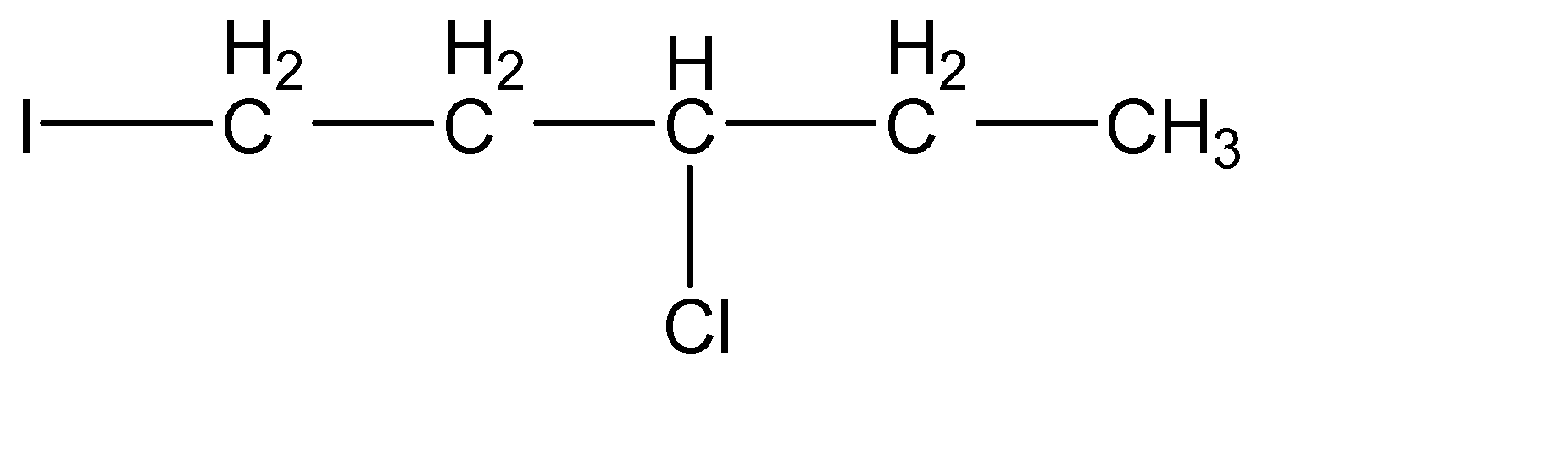
(c)
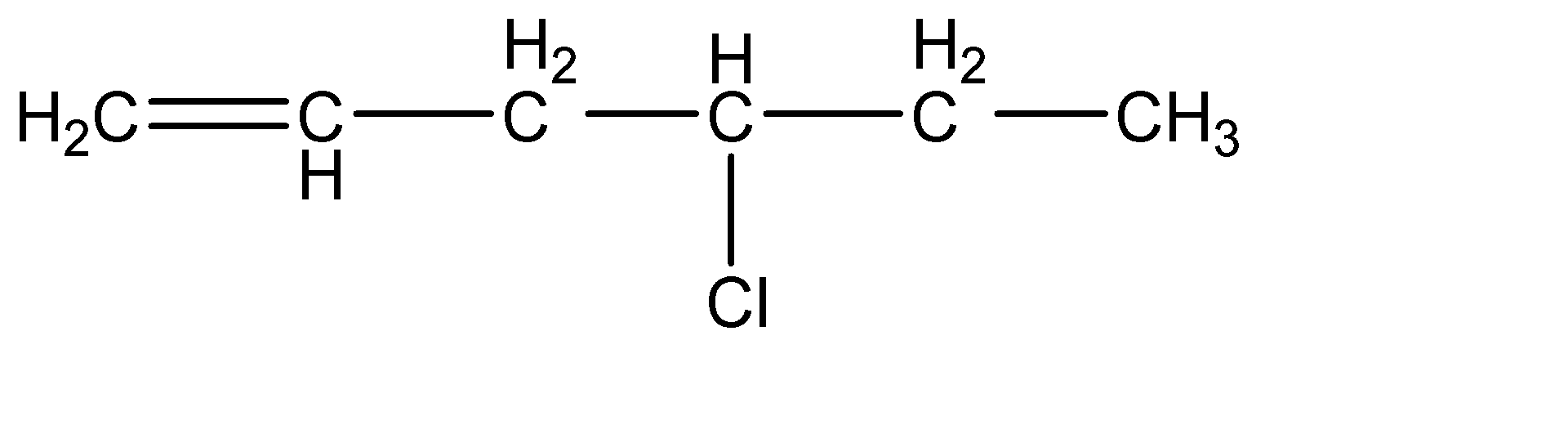
(d)
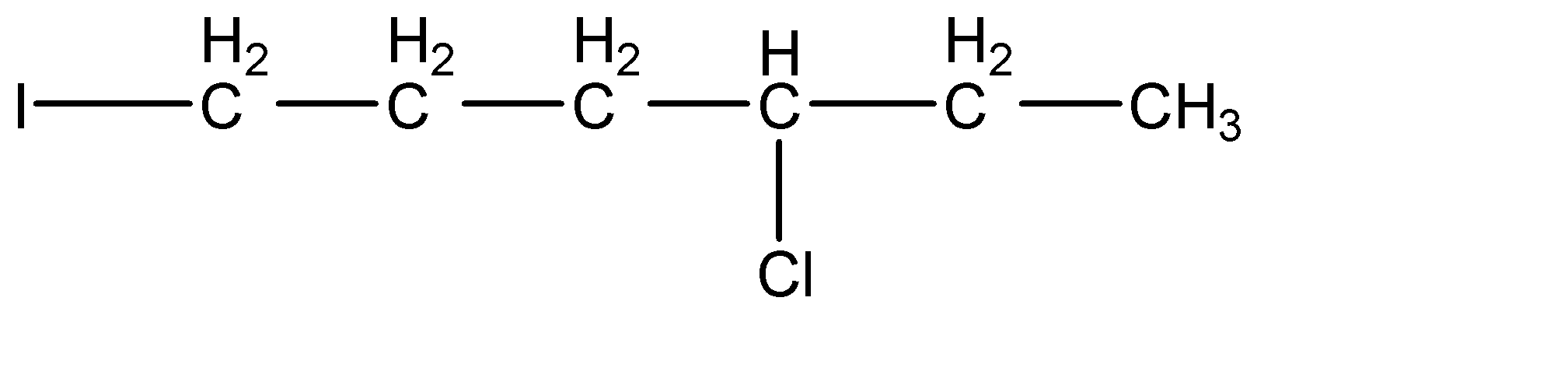
Solution
The above reaction goes through the SN2 reaction mechanism. As we know that the SN2 reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which a bond is broken and another is formed simultaneously. Two reacting species are involved in the rate determining step of the reaction that takes place.
Complete answer:
Let us first discuss about SN2 reaction mechanism as follows:-
-SN2 reaction mechanism: It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which a bond is broken and another is formed simultaneously. Two reacting species are involved in the rate determining step of the reaction that takes place. It is also known as bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, associative substitution, and interchange mechanism.
-When sodium iodide (NaI) is mixed in acetone, it gets completely soluble in it and hence breaks into Na+ and I− ions where iodide ion act as a nucleophile during the reaction.
-The reaction takes place as follows:-
-As we can see that iodide ion (I−) acts as a nucleophile and attacks at the carbon site where the leaving group i.e., chloride (-Cl) group is attached. They form a transition state where Chlorine atom is leaving and iodine is attaching itself to the carbon and at the end we obtain 1-iodo-4-chlorohexane.
- After this the chloride ion interacts with sodium ion and forms sodium chloride (NaCl).
-Also iodide ion (I−) attacks the chlorine of carbon-1 than chlorine at carbon-2 because SN2 mechanism prefers primary site over secondary site due to hindrance reasons.
Hence, the product of the reaction is (d) .
Note:
-As sodium iodide is more soluble in acetone as compared to sodium chloride which is least soluble in it, so we will also obtain NaCl as precipitate during the reaction.
-SN2 reaction mechanism always prefers less hindered sites over more hindered sites.
