Question
Question: Here, P is: \(Glu\cos e\xrightarrow[{(ii)P/HI}]{{(i)HCN/{H_3}{O^ + }}}P\); A: n-heptanoic acid ...
Here, P is: Glucose(i)HCN/H3O+(ii)P/HIP;
A: n-heptanoic acid
B: 2-methyl hexanoic acid
C: n-heptane
D: 2-methyl hexane
Solution
Glucose is actually a monosaccharide consisting of the six carbon atoms along with one aldehyde group. Therefore, we can say glucose is an aldohexose. In the present question, you can recall the principal of Kiliani–Fischer synthesis method (named after the German chemists namely ‘Heinrich Kiliani’ and ‘Hermann Emil Fischer’) for the synthesis of monosaccharides.
Complete step by step answer:
Through the Kiliani-Fischer synthesis method, we can increase the length of the carbon chain of a sugar molecule by appending or adding an additional atom of carbon to the sugar molecule. The synthesis reaction initiates with the reaction of glucose with the hydrogen cyanide. Then this cyanide undergoes the nucleophilic addition to carbonyl group of the sugar (glucose in the present case existing mainly in the form of cyclic hemiacetal, and it is always in the chemical equilibrium with the open-chain aldehyde form) and it results in the formation of glucose cyanohydrin. Glucose cyanohydrin hydrolysis cyanide into a carboxylic acid group in order to form a glucoheptonic acid which then undergoes reduction with the hydriodic acid in the presence of red phosphorous finally yields heptanoic acid. As a result the carbon chain length of the sugar is increased by one carbon atom. The reaction is depicted below:
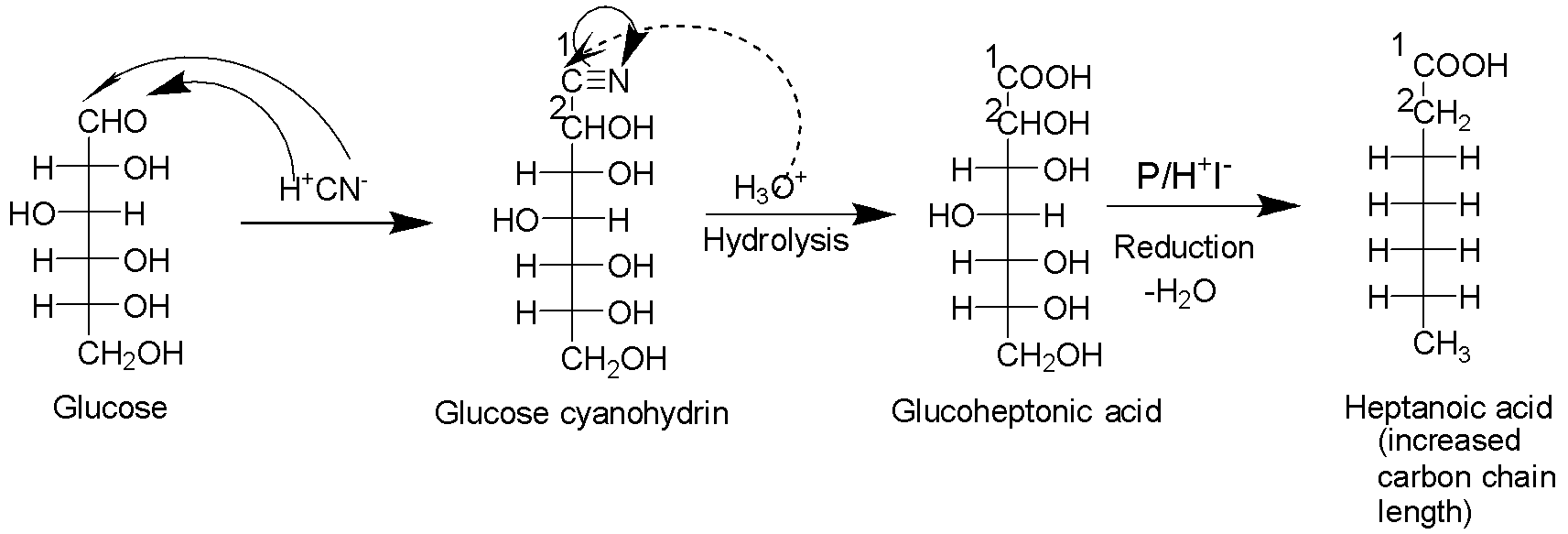
As can be seen above, Kiliani-Fischer synthesis is a series of reactions which extends the chain of carbon by one carbon in a carbohydrate.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Opposite to Kiliani-Fischer synthesis method, there exists a Ruff Degradation method in which length of the carbohydrate can be shortened (instead of increased) by a single carbon atom. The Ruff Degradation method performs the reverse reaction in which sugar is oxidized to carboxylic acid in the presence of bromine water and then undergoes oxidation in the presence of iron sulfate and oxygen with liberation of CO2.
