Question
Question: Here,N – O – N bond angle is maximum in: A. \(N{{O}_{2}}^{+}\) B. \(N{{O}_{2}}\) C. \(N{{O}_{3...
Here,N – O – N bond angle is maximum in:
A. NO2+
B. NO2
C. NO3
D. N2O3
Solution
Bond angle is the angle between two adjacent atoms. The valence electrons of an atom are distributed as bond and lone pairs on a covalent molecule. These bond and lone pairs affect the bond angle of any molecule. This is according to the VSEPR theory, that the bond and lone pair of electrons decide the geometry of atoms and hence the bond angles.
Complete answer:
The shapes of molecules tell us the bond angles between them. These shapes are identified using VSEPR theory that stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory suggests that a shape of a molecule is dependent on the valence pair of electrons in the atoms of that molecule. These valence electrons are distributed in the form of bond pairs and lone pairs. The interactions of these pairs are in the order, lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair > bond pair – bond pair. This states that lone pair lone pair interaction is more due to which the shape of the molecule distorts and the bond angle changes.
The shape of NO2+ is linear as the valence electrons are distributed as two double bond pairs, as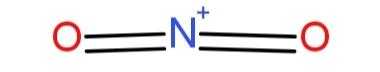 This linear arrangement of the molecule is due to the repulsions between the electron rich regions, so it has a bond angle of 180∘.
This linear arrangement of the molecule is due to the repulsions between the electron rich regions, so it has a bond angle of 180∘.
While,NO2 structure 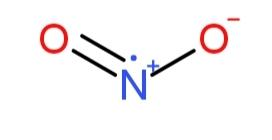 consists of an extra electron pair so, electron density due to the absence of 2 double bonds creates less repulsion, so it does not have maximum bond angle as the angle is 134∘.
consists of an extra electron pair so, electron density due to the absence of 2 double bonds creates less repulsion, so it does not have maximum bond angle as the angle is 134∘.
NO3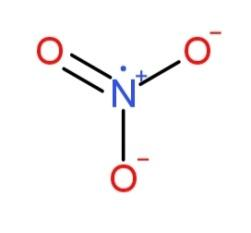 And N2O3
And N2O3 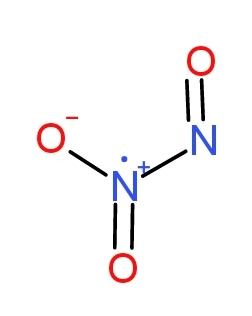 has bond angles of 120∘ and 130∘ respectively.
has bond angles of 120∘ and 130∘ respectively.
So, the N – O – N bond angle is maximum in NO2+.
Therefore option A is correct.
Note:
NO3 has trigonal planar geometry that makes the angles 120 degree. The VSEPR theory suggests that the presence of lone pairs and bond pairs create repulsions to the extent that they change the shape of any molecule. The NO2+ molecule consist of one electron less on nitrogen due to which the double bonds are formed that makes the shape linear.
