Question
Question: he number of chiral carbons in \(\beta\) -D(+)-glucose is: A.5 B.6 C.3 D.4...
he number of chiral carbons in β -D(+)-glucose is:
A.5
B.6
C.3
D.4
Solution
In order to solve the question, first understand the concept of chirality. Then find out the meaning and criteria of assigning a chiral carbon or an asymmetric carbon atom. Draw the structure of the given compound in Haworth projection and then mark the chiral carbons present in it.
Complete answer:
- Chirality is the property of asymmetry in a molecule or any substance.
- If the mirror image of a substance is non-superimposable with that substance then, that substance is said to process chirality and the substance is said to be chiral or asymmetric. It is represented by an asterisk sign (*).
- For example, the letter ‘A’ has the mirror image ‘A’ only so both the images can be superimposed as one image. So, the letter ‘A’ is not chiral or achiral.
- For letter ‘B’ or ‘D’ or ‘P’, its mirror images are non-superimposable to each other and therefore, these letters are chiral and enantiomers of each other.
- In chemistry, a chiral carbon is the one which has four different substituents attached to it.
- If the carbon is unsaturated then it is achiral only because during unsaturation, two or three bonds are formed with the same substituent.
- The structure of β -D(+)-glucose is shown below,
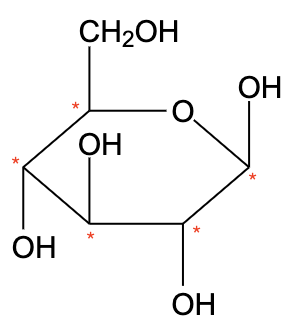
- Glucose has six carbon atoms. -D-glucose does not have a plane of symmetry and thus, the carbon atoms are different.
- β -D(+)-glucose has 5 chiral carbons.
Thus, the correct option is (A).
Note:
Chiral carbon atoms are the carbon atoms which lack symmetry and have four different substituents attached to it. Chiral carbon is also known as asymmetry carbon. Enantiomers are pairs of compounds which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
