Question
Question: Halogenation of alkene using \( B{r_2}/CC{l_4} \) is syn addition but not anti addition. If this is ...
Halogenation of alkene using Br2/CCl4 is syn addition but not anti addition. If this is true enter1, else enter 0.
Solution
When halogen is added on the same side of the alkene, it undergoes syn addition. When halogen is added on the opposite side of the alkene, it undergoes anti addition. If we know this basic, solution to the question becomes easy to handle.
Complete step by step answer:
Elements like chlorine and bromine are e− loving species. They are called electrophiles. Breaking the double bond ( π -bond) of alkenes, these electrophiles when added to the alkenes produces vicinal dihalides (halogens like Br2,Cl2 in molecular form). Br2,Cl2 are the best choice of halogens for halogenation of alkenes.
−C=C−+Br2CCl4 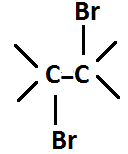
Alkene Bromine 1,2-vicinal dibromide
When Br2/CCl4 is added into the alkenes, bromonium ion and bromide ion are produced with partial positive and partial negative charge respectively. These induced dipoles are formed due to π−e− cloud of alkene. This bromonium ion attacks the alkene and forms a bond with one of the atoms which leads to formation of a highly unstable intermediate. However, the bromide ion then attacks the intermediate from the opposite side and forms1,2-dibromide (trans- dibromo products) that are highly stable.
Since the attack is from the opposite side, so the anti addition is followed.
So, the given statement is false and the value entered is 0.
Note:
Fluorine reacts vigorously and forms many side products whereas addition of iodine is thermodynamically not supported. When Br2 reacts with CCl4 , dipole induced dipole interactions between the molecules occur that lead to formation of Br+ and Br− ions. This helps in electrophilic addition reactions in alkenes.
