Question
Question: Graphite is This question has multiple correct options A. A good conductor B. \(s{p^2}\) hybri...
Graphite is
This question has multiple correct options
A. A good conductor
B. sp2 hybridised
C. An amorphous solid
D. A covalent crystal
Solution
It is referred to as plumbago, it is a crystalline form of the element carbon with its atom arranged in hexagonal structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Graphite is composed of flat two dimensional sheets of carbon atoms. Each sheet is a hexagonal net of C atoms, and may be regarded as a fused system of benzene rings. The layers are held together by relatively weaker van der waals force.
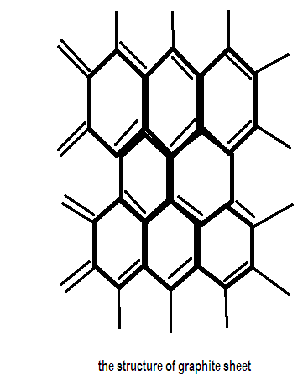
Graphite and diamonds are the only two naturally formed polymers of carbon. Graphite is essentially a two dimensional, planar crystal structure. Soft,greasy dark grayish coloured crystalline solid.
Carbon in graphite has a sp2 type of hybridization and is linked to three other carbon atoms in a hexagonal planar structure. Since only three of the valence electrons of each carbon atom are involved the remaining unhybridized p orbital of each carbon atom having an electron overlaps with its counterparts of the adjacent carbon atoms in the same layer to form pi-bonds. Hence the pi-electrons are delocalized in the whole sheet which is why Graphite is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity and has the highest natural strength and stiffness of any material and is very resistant to chemical attack.
At the same time, it is one of the lightest of all reinforcing agents and has high natural lubricity. Graphite is a covalent crystal and crystalline. It is quite hard because of the strong covalent bonding throughout the lattice.
Hence the correct option are A,B and D.
Note:
It occurs naturally in hexagonal structure under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. Graphite is used in pencils and lubricants. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity. Its high conductivity makes it useful in electronic products such as electrodes, batteries, and solar panels.
