Question
Question: Going from fluorine, chlorine, bromine to iodine the electronegativity: A. Increases B. First de...
Going from fluorine, chlorine, bromine to iodine the electronegativity:
A. Increases
B. First decreases then increases
C. Decreases
D. Changes randomly
Solution
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons to itself. Size is a crucial factor in determining the electronegativity of an atom. There are some exceptions also which you have to remember.
Complete step by step solution:
First let us discuss electronegativity and see which factors are responsible in determining the electronegativity.
Electronegativity is just a tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself. More the electronegativity of an atom , the more its electron attracts to itself. Electronegativity of an atom depends upon its ionization energy and its electron affinity.
Small atoms have higher electronegativity because the atoms which have nearly filled shells of electrons have higher electronegativity than those with less than half filled.
Factors affecting electronegativity:
1. Atomic Size: The smaller the size of an atom the greater its tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons. So smaller atoms have more electronegativity.
2. Number of inner shells: The atom with the greater number of inner shells has less value of electronegativity than the atom with smaller number of inner shells.
Now let's move to the question so we are going from top to bottom in a group and so size is increases and no. of inner shells also increases and moreover the nuclear charge is decreasing which results in the decrease in electronegativity.
So as we move down the group from fluorine, chlorine, bromine to iodine the electronegativity decreases.
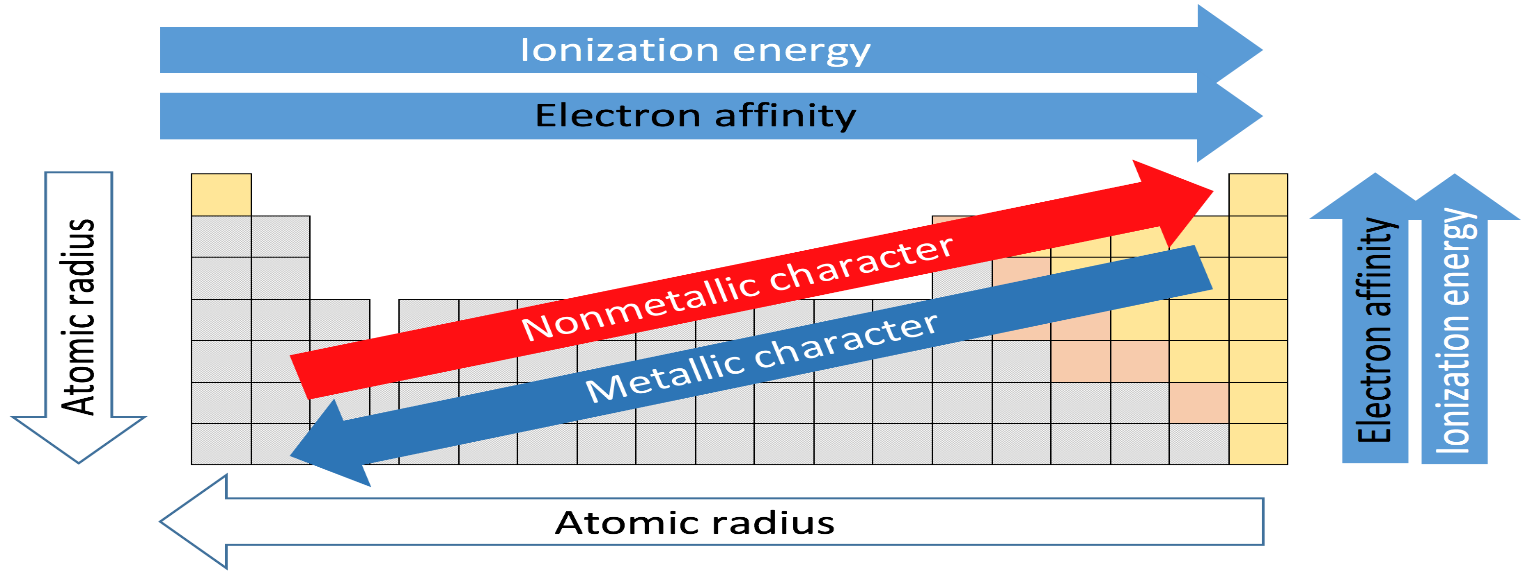
Hence our correct option is C.
Note:
Nuclear charge decreases down the group due to no. of shells increases so its shielding effect on outer valence electrons decreases and hence electronegativity decreases.
