Question
Question: Glucose has _____ optical isomers. A.4 B.8 C.16 D.10...
Glucose has _____ optical isomers.
A.4
B.8
C.16
D.10
Solution
We know the molecules which have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms are called isomers. There are two types of isomers,
-Structural isomers
-Stereoisomers
We have to remember that molecules with the same chemical formulas but differ structurally in the sequence in which the atoms are linked are called structural or constitutional isomers.
Optical isomers are compounds which have the same molecular formula, atoms and bonds but different spatial arrangement of atoms and non-superimposable mirror images.
Formula Used: Number of optical isomers = 2n, where n is the number of chiral carbons.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with discussing the optical isomer for better understanding of the question. Optical isomers are compounds which have the same molecular formula, atoms and bonds but different spatial arrangement of atoms and non-superimposable mirror images. Each non-superimposable mirror image is called an enantiomer.
We are provided with a molecule of glucose and for determining the optical isomers of such compounds we use the formula,
Number of optical isomers = 2n, where n is the number of chiral carbons.
We can draw the structure of D-glucose as,
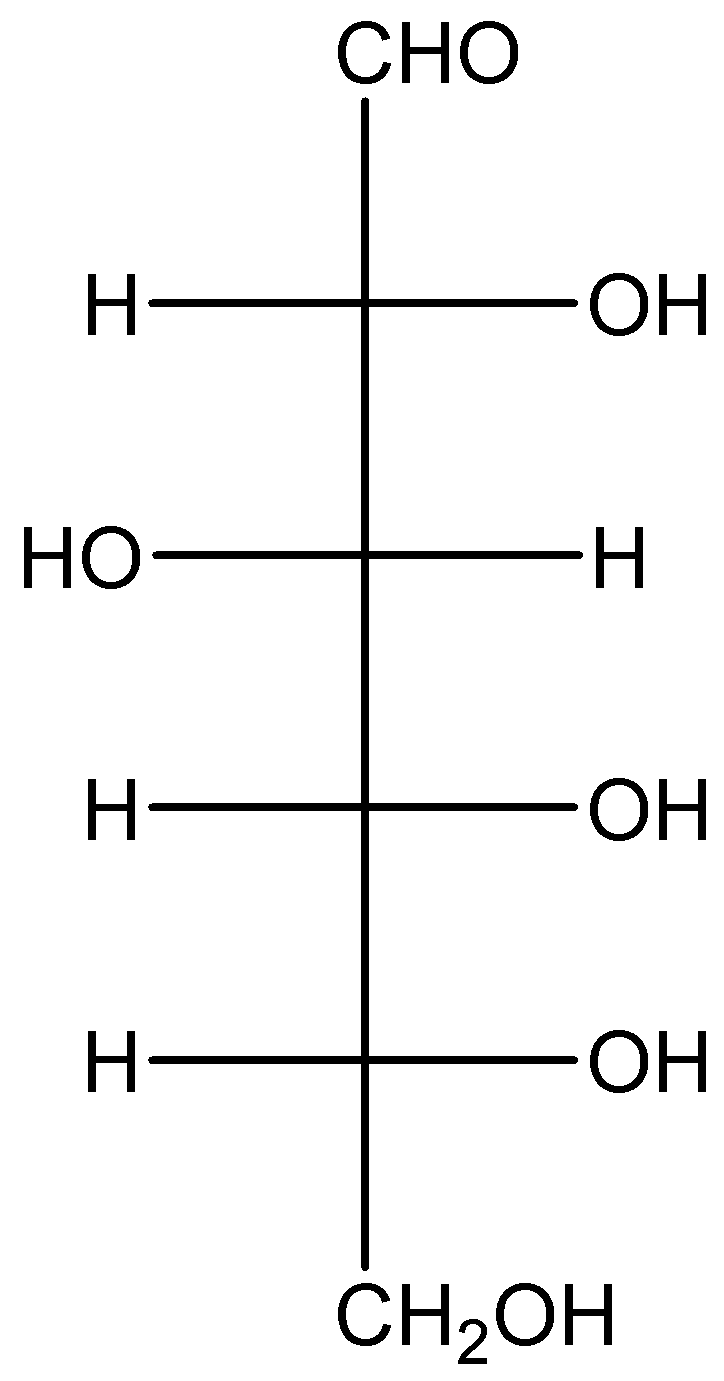
In case of glucose the number of chiral carbon is 4, which means that the whole molecule can revolve around any of these 4 carbons. Putting this in the formula we get
Number of optical isomer 2n=24=16
Hence the answer to this question is option C. 16. Glucose has 16 optical isomers.
Note: We have to remember that the glucose is a monosaccharide and it is the most abundant polysaccharide present on earth. It is the monomer unit of starch and other big polysaccharides. Also the food that we eat is broken into the glucose before converting into energy. It is mainly made by plants and algae during photosynthesis.
We can classify the stereoisomer into three categories,
-Chain isomerism
-Position isomerism
-Functional group isomerism
Chain isomerism:
We must remember that in chain isomerism the skeletons are reordered to create different structures.
Position isomerism:
We have to know that in position isomerism the atom changes the position on the parent atom.
Functional isomerism:
We have to remember that functional isomerism is the structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but the atoms are connected in different ways.
