Question
Question: Giving reasons, state the ‘signs’ (positive or negative) which can be given to the following: (a) ...
Giving reasons, state the ‘signs’ (positive or negative) which can be given to the following:
(a) Object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror.
(b) Image distance (v) for a concave mirror.
(c) Image distance (v) for a convex mirror.
Solution
For a spherical mirror, the distances generally are measured from the midpoint of the mirror. Distances mean the object distance, image distance, and focal length. The two types of spherical mirrors are concave and convex. The ray diagrams have to be drawn to understand the process of taking signs of those distances. Note that, the signs are taken based on the direction of light.
Complete step by step answer:
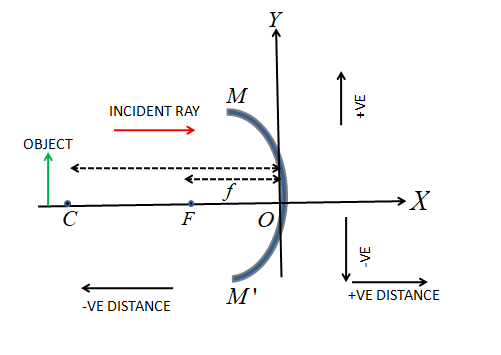
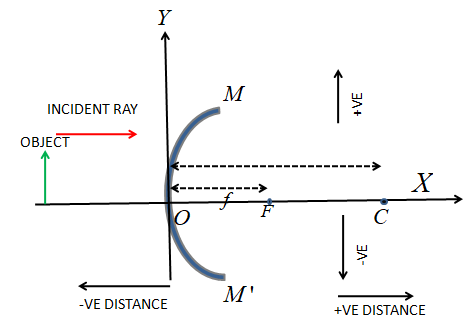
The sign convention for a spherical mirror is called the Cartesian sign convention. The rules are:
The distances are measured generally from the pole or the midpoint of the spherical mirror.
The distance measure from the pole is positive if it is directed towards the incident ray and negative if it is away from the incident ray.
If the principal axis is X, the distance along the positive Y-axis (perpendicular to the X-axis) is taken as positive and the distance along the negative Y-axis is taken as negative.
These rules are applicable for both of the two spherical mirrors: convex and concave.
Let us draw the ray diagram for the two mirrors.
Concave mirror:
Convex mirror:
Based on the convention rule and the ray diagrams we can create a chart:
| Mirror types | Object distance (u) | Real Image distance (v) | Virtual image distance (v) |
|---|---|---|---|
| concave | (-ve) | (-ve) | (+ve) |
| convex | (-ve) | Does not exist | (+ve) |
Therefore, we can conclude
(a) sign of object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror: negative.
(b) sign of image distance (v) for a concave mirror: it creates both real and virtual images. For a real image, the sign is negative and for a virtual image, the sign is positive.
(c) sign of image distance (v) for a convex mirror: it only creates a virtual image and the sign is positive.
Note:
From the sign convention the sign of focal length, radius of curvature of the mirror, the heights of the object and mirror are also taken.
For a concave mirror,
- The sign of focal length is negative.
- The sign of radius of curvature is negative.
- The sign of the height of the object is positive.
- The sign of the height of the real image is negative and the virtual image is positive.
For a convex mirror,
- The sign of focal length is positive.
- The sign of radius of curvature is positive.
- The sign of the height of the object is positive.
- The sign of the height of the virtual image is positive.
