Question
Question: Given two functions \(f\left( x \right)\text{ and }g\left( x \right)\) . For what x does the equatio...
Given two functions f(x) and g(x) . For what x does the equation f′(x)=g(x) hold true?
f(x)=sin32x and g(x)=4cos2x−5sin4x .
Solution
Start by finding the derivative of x using chain rule of differentiation followed by substituting it along with g(x) in f′(x)=g(x) . Use the formula that sin4x=2cos2xsin2x and take cos2x common from the right hand side. Cancel cos2x from both sides and solve the quadratic equation to get the values of x. Remember that the general solution of sinx=siny is x=nπ+(−1)ny and of cosx=cosy is x=2nπ±y.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before moving to the solution, let us discuss the periodicity of sine and cosine function, which we would be using in the solution. All the trigonometric ratios, including sine and cosine, are periodic functions. We can better understand this using the graph of sine and cosine.
First, let us start with the graph of sin x.
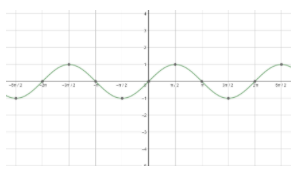
Next, let us see the graph of cos x.
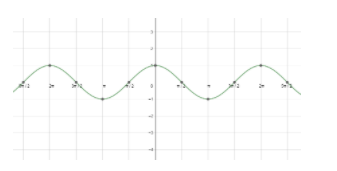
Looking at both the graphs, we can say that the graphs are repeating after a fixed period i.e. 2πc . So, we can say that the fundamental period of the cosine function and the sine function is 2πc=360∘
Now let us start the solution to the above question by finding the derivative of f(x).
f(x)=sin32x
Applying chain rule of differentiation and using the formula dxd(sinx)=cosxdx , we get
f′(x)=3×2×sin22x×cos2x=6sin22xcos2x
Now we will start solving the equation f′(x)=g(x) .
6sin22xcos2x=4cos2x−5sin4x
We know that sin4x=2cos2xsin2x . So, using this in our equation, we get
6sin22xcos2x=4cos2x−5×2sin2xcos2x
⇒6sin22xcos2x=(2−5sin2x)×2cos2x
Now we will cancel cos2x from both sides. But if cos2x is zero, both sides become zero, so, one of the solutions to the above equation is cos2x= 0 and we know that cos2π=0 .
∴cos2π=cos2x
We know that the general solution of cosx=cosy is x=2nπ±y .
∴2x=2nπ±2π
⇒x=nπ±4π
Now let us again move to the parent equation and consider the case when cos2x is not equal to 0.
6sin22xcos2x=(2−5sin2x)×2cos2x
⇒3sin22x=2−5sin2x
⇒3sin22x+5sin2x−2=0
So, the equation is a quadratic equation in sin2x. So, we can write 5 as 6-1. On doing so, we get
3sin22x+6sin2x−sin2x−2=0
⇒3sin2x(sin2x+2)−1(sin2x+2)=0
⇒(3sin2x−1)(sin2x+2)=0
Now the factor (sin2x+2) is of no use, as sine cannot have a value of -2 as it is always greater than -1. So, let us solve the other factor.
3sin2x−1=0
⇒sin2x=31
Now this can be written as:
sin2x=sin(sin−131)
We know that the general solution of sinx=siny is x=nπ+(−1)ny .
∴2x=nπ+(−1)nsin−131
⇒x=2nπ+2(−1)nsin−131
So, the solutions to the above question is x=nπ±4π and x=2nπ+2(−1)nsin−131 , where n can be any integer number.
Note: Be careful about the calculation and the signs of the formulas you use as the signs in the formulas are very confusing and are very important for solving the problems. Also, remember that 31=sin(sin−131) is a complete result but 2x=sin−1(sin2x) is not always correct. Also, don’t forget the solutions coming from the cos2x part, as it is cancelled.
