Question
Question: Given,\(^{{\text{227}}}{\text{Ac}}\) has a half-life of \(22\) years with respect to radioactive dec...
Given,227Ac has a half-life of 22 years with respect to radioactive decay. The decay follows two parallel paths: 227Ac→227Th and 227Ac→227Fr. If the percentage of the two daughter nuclides at 2.0 and 98.0 respectively, the decay constant (in year-1) for 227Ac→227Th path is closest to
A) 6.3×10−2
B) 6.3×10−3
C) 6.3×10−1
D) 6.3×10−4
Solution
Radioactive decay has two important terms related to it, Half-life and Decay constant. we'll define both the terms and can find a relation between the 2 . The relations are often obtained by using the expression of decay law.
Complete step by step answer:
Radioactive decay is described because the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A sample material containing radioactive nuclei is taken into account radioactive. The decay of radioactive elements occurs at a hard and fast constant rate. The half-life of a radioisotope is the time required for one half the concentration of the unstable substances to degrade into a more stable material. We will say that half-life is the time required for a radioactive sample to scale back to half its initial value. The half-life of a radioactive sample is represented by T1/2.Decay constant is that the proportionality between the dimensions of a population of radioactive atoms and therefore the rate at which the population decreases due to decay. The decay constant is represented by the symbol λ.
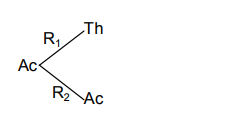
Now we calculate the % of Th
%Th = RTR1 = 1002
Similarly we calculate the % of Ac
%Ac = RTR2 = 10098
∴R2R1=982
Hence RT = R1 + R2
220.693=R1 + 298R1
∴R1=6.3×10−4
Hence the correct option is answer D.
Note:
Half-life means how much time a radioactive sample takes to become half of its original concentration, while decay constant is a probability of decay per unit time. Half-life of a radioactive sample depends on the elimination rate of sample and the initial concentration of the sample, while decay constant is fixed for a particular radioactive nuclide.
