Question
Question: Given,\({{N}_{2}}\) gas will not be evolved upon the reaction of \(HN{{O}_{2}}\) with which of the f...
Given,N2 gas will not be evolved upon the reaction of HNO2 with which of the following amines?
(A)- 1o
(B)- 2o
(C)- 3o
(D)- Both B and C
Solution
Primary (1o), secondary (2o) and tertiary (3o) amines, all react with nitrous acid (HNO2) but in different ways. Alkane Diazonium salts are very unstable and decompose to give alcohols and release nitrogen (N2) gas. Diazonium salts are formed from primary amines only.
Complete answer:
Both aromatic and aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts at 273 -278 K temperature. Nitrous acid is quite unstable and thus it is generally formed immediately before its use in a reaction.
Reaction of aromatic primary amines with cold solution of nitrous acid to form arenediazonium salts is called diazotization. On increasing the temperature above 278 K, diazonium salts decompose with the evolution of N2 gas to form phenols. The chemical reaction of aniline aromatic (1o aromatic amine) with HNO2 is given below:
NaNO2+HCl→HNO2+NaCl
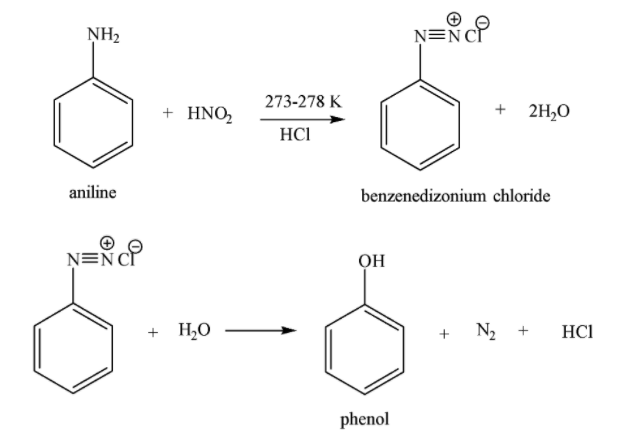
Similarly, aliphatic 1o amines react with HNO2 to form alkane diazonium salts which are unstable even at low temperature and thus decompose immediately to form alcohol and evolve N2 gas.
R−NH2+HNO2273−278KR−OH+N2+H2O
Secondary amines react with nitrous acid to form yellow coloured oily compounds called N-nitrosamines which are insoluble in mineral acids. Both aromatic and aliphatic 2o amines form these oily compounds with HNO2. Reaction of 2o amine with HNO2 is given below:
R2NH+HNO2273KR2N−NO+H2O
Tertiary amines form ammonium salts with nitrous acid. Aromatic 3o amines form nitroso (−N=O) substituted compounds whereas aliphatic 3o amine form water soluble nitrite salts.
Aromatic 3o amines:
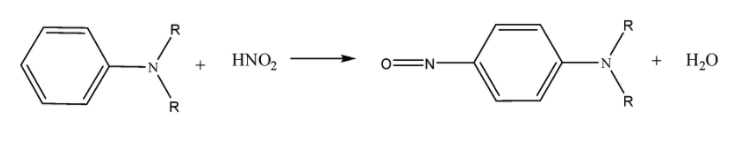
Aliphatic 3o amines:
R3N+HNO2→R3NH+NO2−
From the above discussion, it is clear that only primary (1o) amines evolve N2 gas on reaction with HNO2.
Since N2 is not released upon the reaction of both 2o and 3o amines with HNO2, therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Note that 1o amines immediately evolve N2 on reaction with HNO2 whereas aromatic 1o amines only release N2 at a temperature higher than reaction temperature. Reaction of amines with nitrous acid is often used as a test to distinguish 1o, 2o and 3o amines. In some cases, it is even possible to distinguish aromatic amines from aliphatic amines using HNO2.
