Question
Question: Given,\({{H}_{2}}O\) is dipolar, whereas \(Be{{F}_{2}}\) is not. It is because: A. \({{H}_{2}}O\) ...
Given,H2O is dipolar, whereas BeF2 is not. It is because:
A. H2O involves hydrogen bonding whereas BeF2 is a discrete molecule
B. H2O is linear and BeF2 is angular
C. H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear
D. the electronegativity of F is greater than that of O
Solution
A dipolar molecule is the compound having polarity. Dipole moment means the difference between the magnitude of charge and the distance between the charged atoms. A molecule is considered to be polar and non – polar due to the resultant dipole it possesses. In polyatomic molecules the dipole moment depends on the shape or spatial arrangement of the atoms.
Complete answer:
Dipole moment of any molecule is the product of the magnitude of the charge and the distance between the centre of the positive and the negative charges. This dipole moment denoted asμcan tell us that any molecule is polar (i.e. have a dipole) or not. When the value of the dipole moment is greater than zero, it means the molecule possesses a dipole. When the value ofμis equal to zero, it means the molecule is not polar.
The value of μdepends on the spatial arrangement of atoms in a polyatomic molecule. As the dipole moment is a vector quantity, it depends on the sum of dipole moments of the individual bonds. When μ= 0, it means that the molecule has a linear shape. While the angular or bent shaped molecules possess a dipole.
We have H2O which has an angular or bent structure as
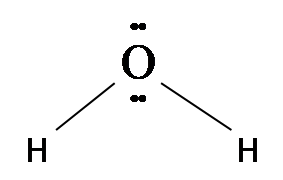
This means it has μ> 0.
While, BeF2 has a linear shape as
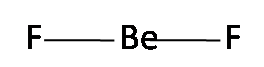
This means that its dipole moment is μ= 0.
Hence, H2O is dipolar, whereas BeF2 is not because H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear.
So, option C is correct.
Note:
The shapes of covalent molecules can be determined through a theory called VSEPR theory that suggests the shape depends on the distribution of valence electrons of the atoms in the form of bond and lone pairs. The repulsion in lone pairs and lone pairs of electrons is the maximum. Water molecule has lone pairs on oxygen that makes its structure bent.
