Question
Question: Given,\(C{H_3}COOH\) is neutralized by NaOH. Conductometric titration curve will be of the a.) ![]...
Given,CH3COOH is neutralized by NaOH. Conductometric titration curve will be of the
a.) 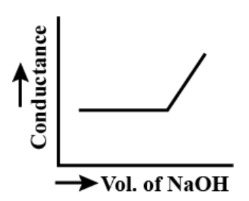
b.) 
c.) 
d.) 
Solution
The acetic acid is weak acid and the sodium hydroxide is a strong base. Its reaction will initially not yield any ion. Thus, the graph will not show any change but later on the hydroxide ions will linearly increase the graph. So, the graph will be linear after complete reaction.
Complete answer:
Conductometric titrations are those in which the electrolytic conductivity of reaction mixture is observed continuously in addition to one reactant slowly.
In the above given reaction mixture, the acetic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide forming sodium derivative of acetic acid and water. The acetic acid is a weak acid but the sodium hydroxide is a strong base.
The acid is the compound which has the ability to donate protons and base is the compound that can donate hydroxide ions. The proton and hydroxide combine giving water with other products.
The electrolytic conductivity is because of the presence of ions. Initially we take acetic acid in a conical flask and slowly start adding sodium hydroxide to it.
When we have not added base, the acetic acid being weak acid will give the proton very low because it dissociates to less extent. When we start adding sodium hydroxide, even then there would be less number of protons because of weak acetic acid. So, the curve will be straight. Once all the acetic acid has been neutralised, then hydroxide ions will not have to combine with any other. So, they will be free. Thus, the conductivity will rise linearly with addition of sodium hydroxide.
So, the curve will rise linearly.
Thus, the correct graph representing is -
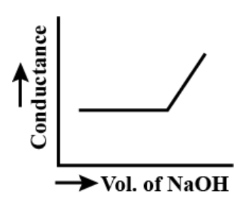
So, the option a.) is the correct answer.
Note:
It must be noted that the acid which can easily dissociate protons is the strong acid and which does not easily dissociate protons is the weakest acid. Same is the case with base. Titration measures the conductance given by electrolyte in the reaction mixture.
