Question
Question: Given,\[but - 2 - ene\] exhibits \[cis - trans\] isomerism due to: A.Rotation around \({C_3} - {C_...
Given,but−2−ene exhibits cis−trans isomerism due to:
A.Rotation around C3−C4 sigma bond
B.Restricted rotation around C=C bond
C.Rotation around C1−C2 bond
D.Rotation around C2−C3 double bond
Solution
We must remember that the similar molecular formula but different compounds are called isomers, similar molecular formula compounds behave as different compounds are called isomerism. The arrangement in the space is different for that compound; it is also known as stereoisomers. There are two types of stereoisomerism called cis-trans and optical isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the cis−trans isomerism (also known as geometric isomerism), occurs in alkene, the carbon in the alkene is bonded two different groups.
but−2−ene structure is,
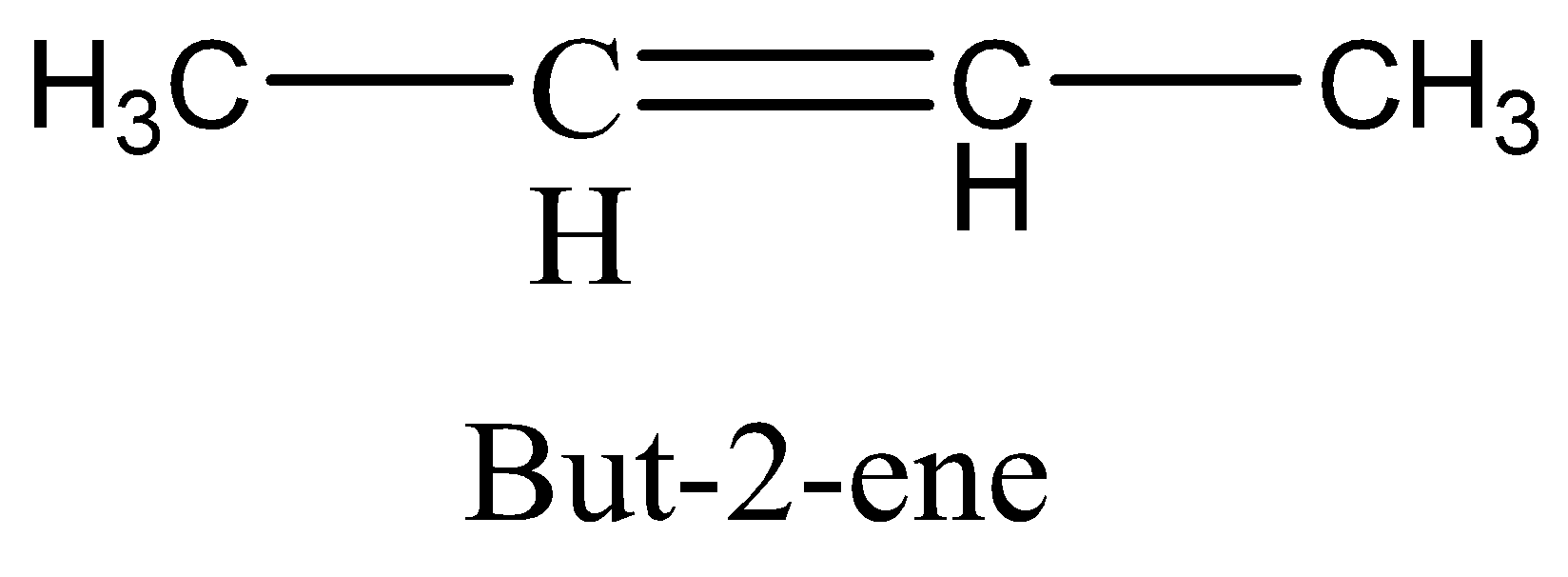
As see above, the methyl and hydrogen group is bonded to different carbon atoms, but this compound has two different structures as follows,
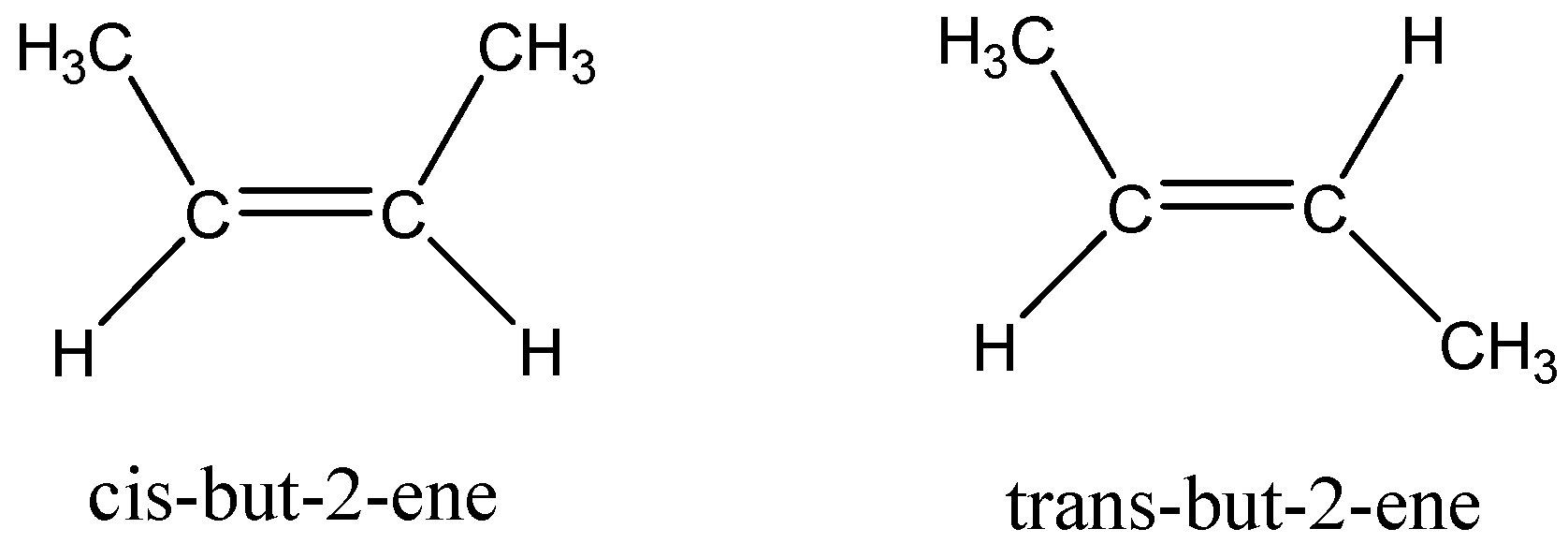
The two methyl groups on the same side in the molecule is cis isomer, called cis - but - 2 - ene and the two methyl groups on opposite side of the molecule is known as trans isomer, then the molecule is called trans - but - 2 - ene .
Let us see the options one by one to find the correct answer,
Option A. Rotation around C3−C4 sigma bond
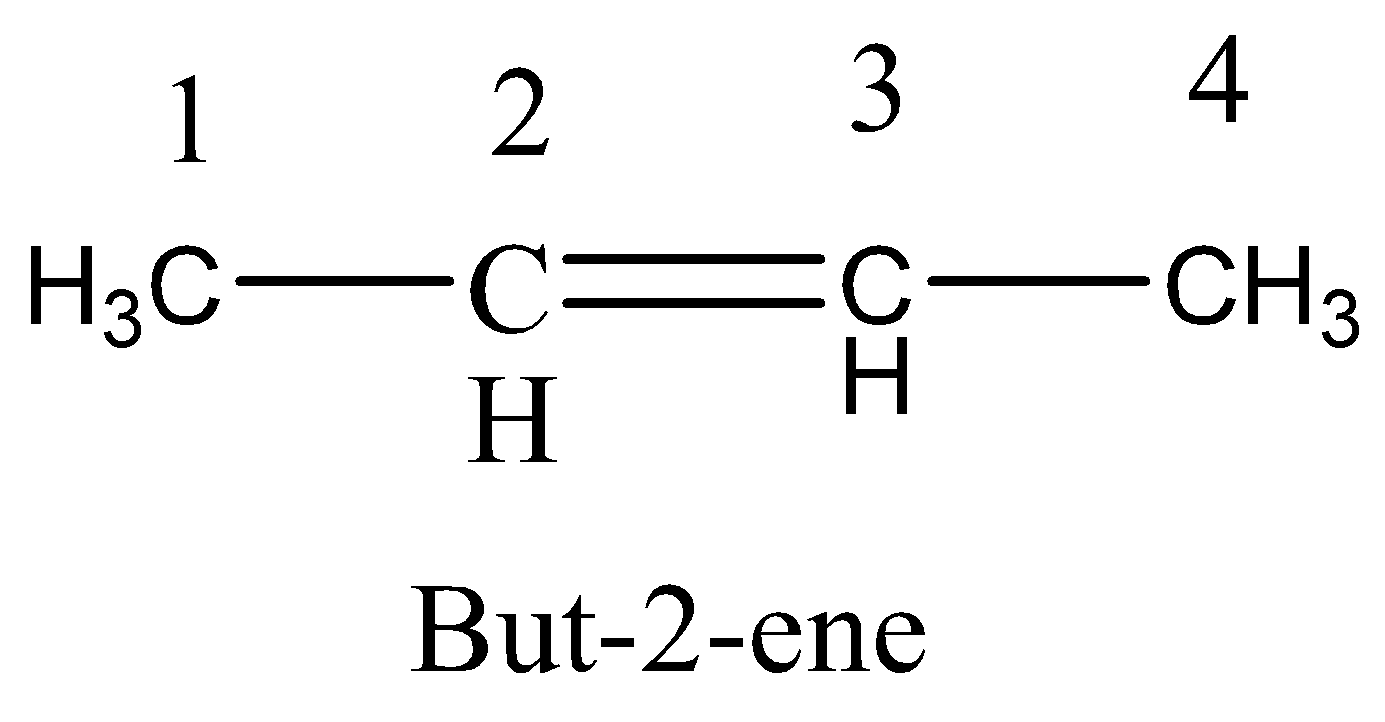
If the rotation around C3−C4 sigma bond, then there is no possible trans isomer. And so, there is no possible for cis−trans isomerism.
Option B. Restricted rotation around C=C bond
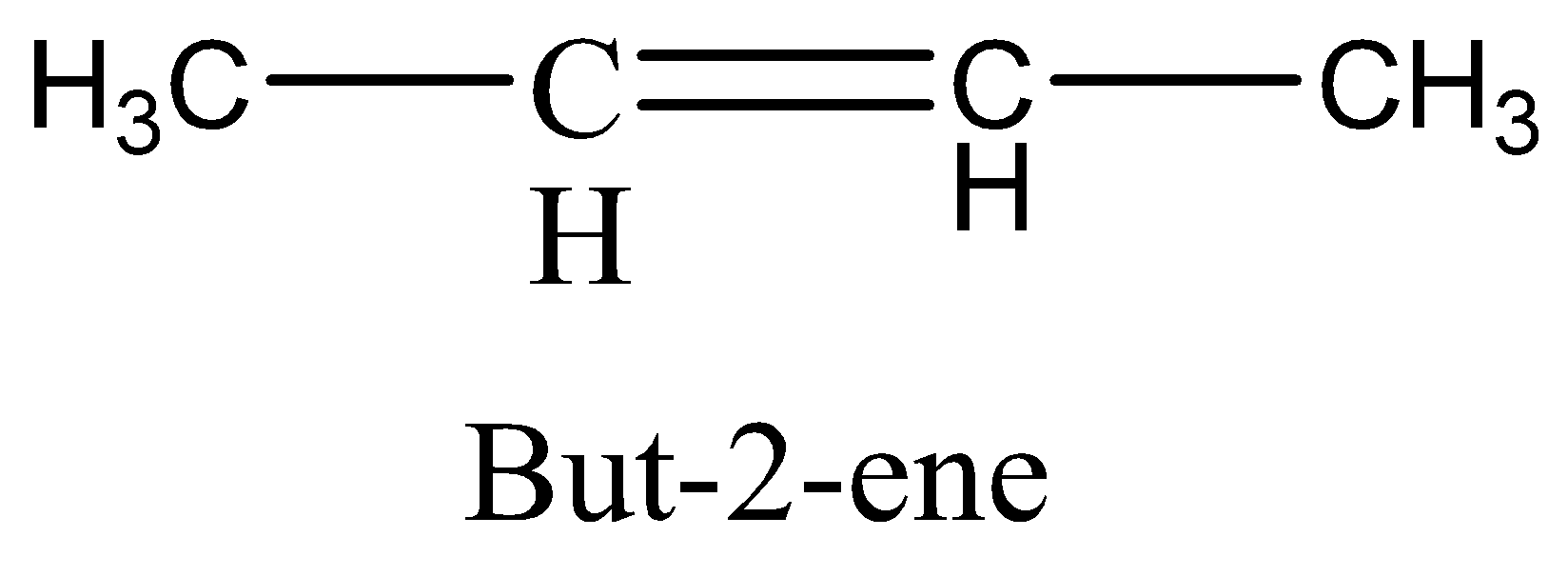
If the rotation is restricted on the molecule and there are two non-identical groups must be present on each doubly bonded carbon atom, then there should be cis−trans isomerism present. The molecule,
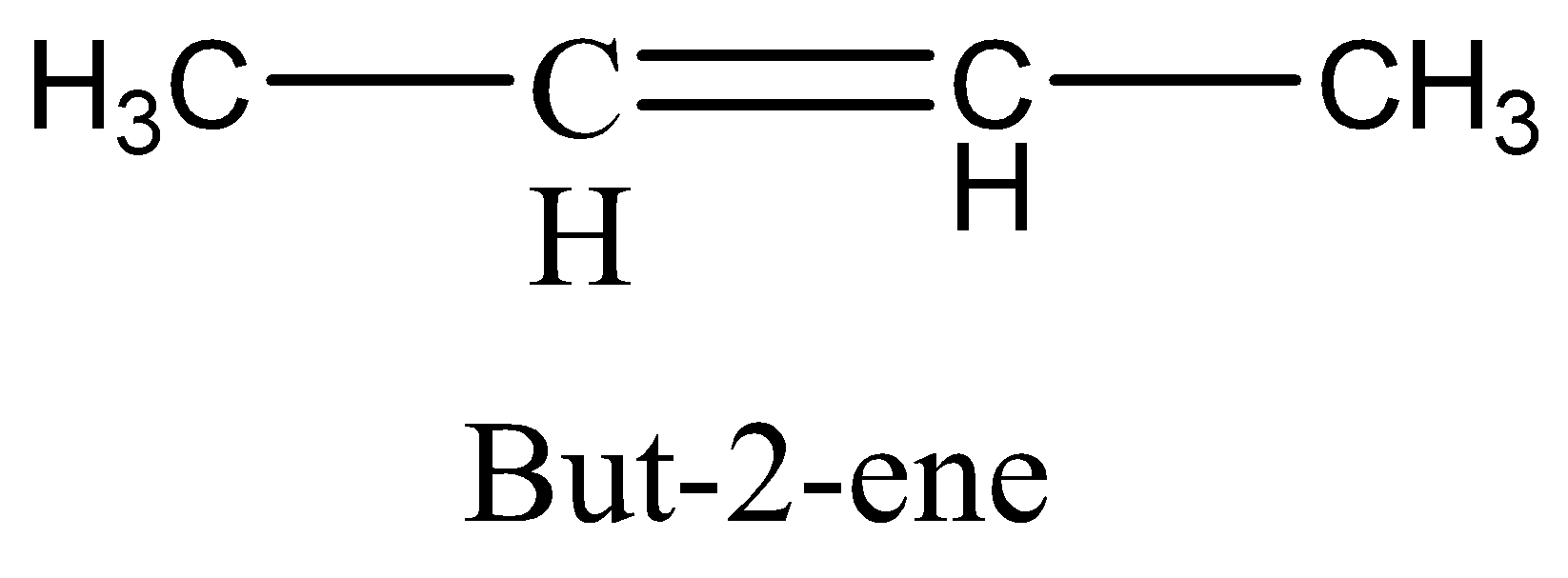
It has restricted rotation in the molecule and there are two non-identical groups present on each doubly bonded carbon atom (C=C bond). So, this is correct option, but we will see the other two options to clarify,
Option C. Rotation around C1−C2 bond
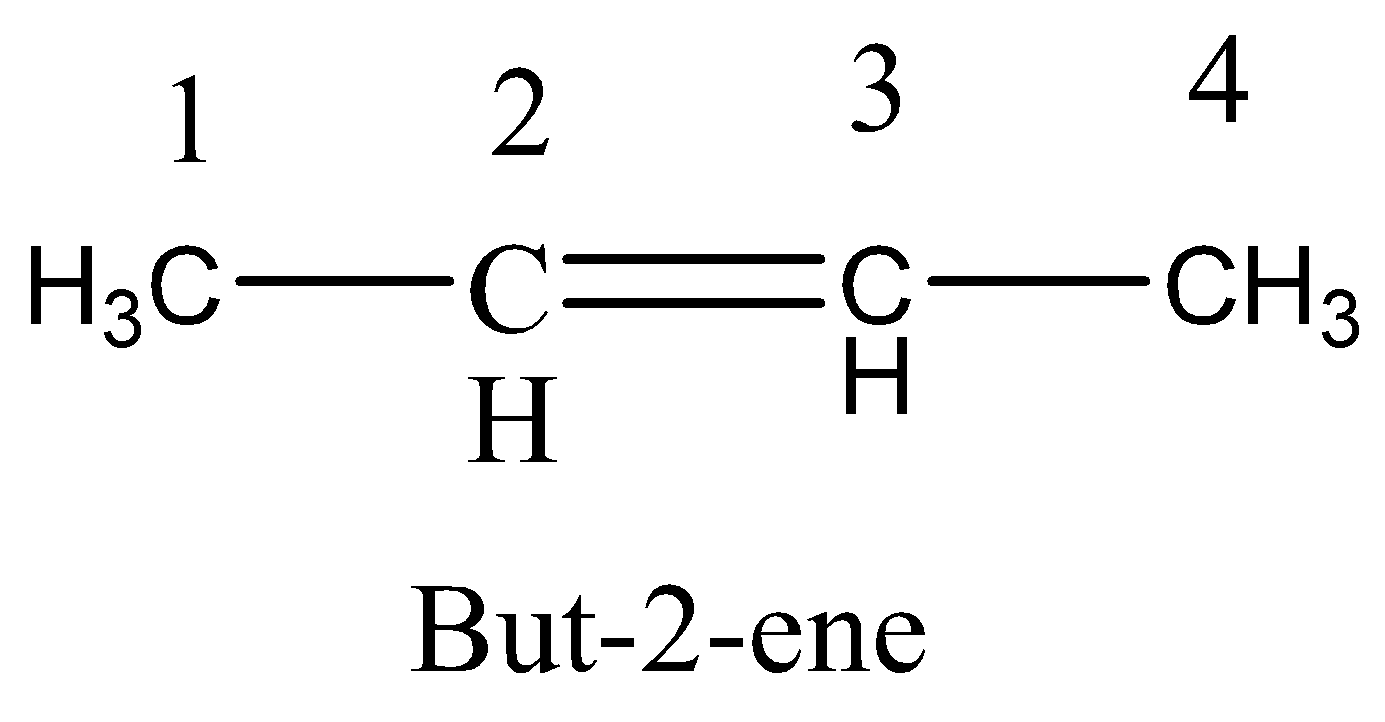
The rotation in the C1−C2 bond does not lead to cis−trans isomerism because C1−C2 bond contains sigma bond. So this is not the correct option.
Option D. Rotation around C2−C3 double bond
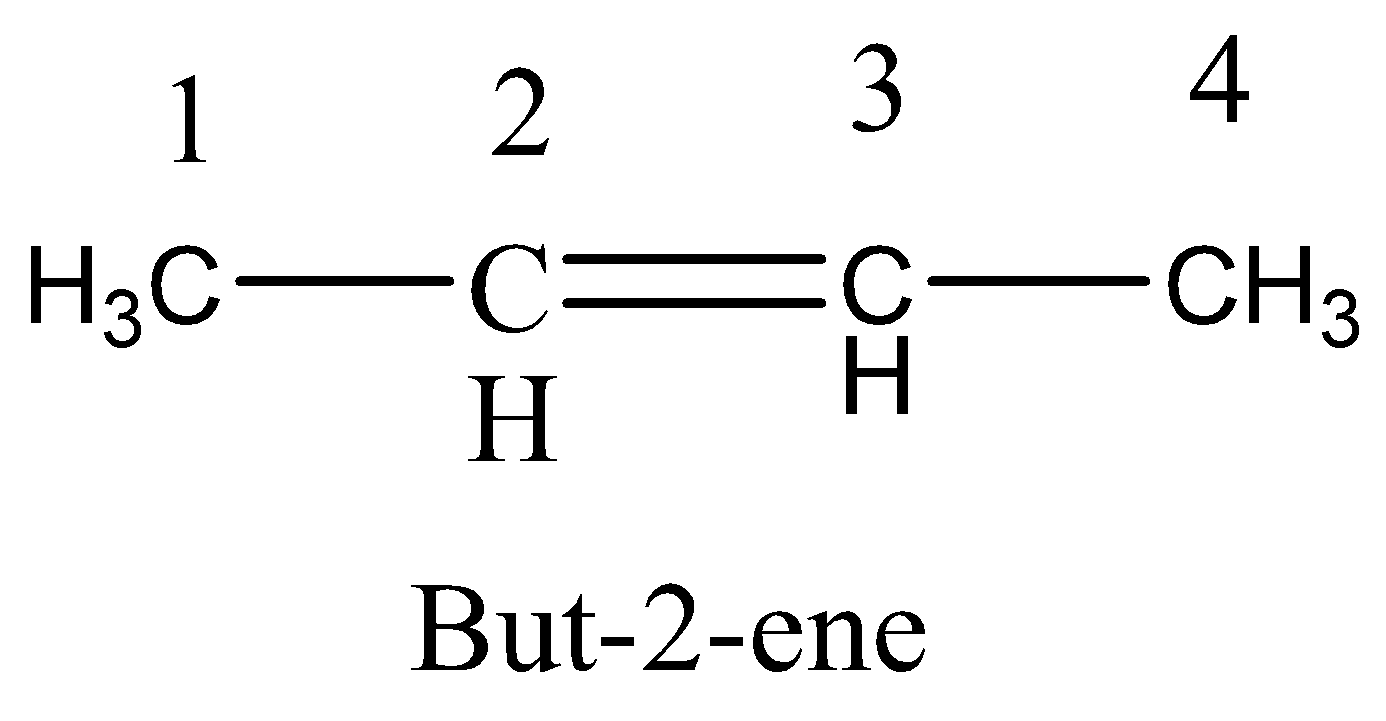
The hybridization in the carbon atom is sp2 and two p orbitals make sidewise overlap.
Two p orbitals make 900 overlap does not twisted, and does not lead to cis−trans isomerism.
From the above information, Option B. Restricted rotation around C=C bond is the correct option.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
We must have to remember that if an alkene contains C=CH2 , then there is no cis−trans isomerism.
In an alkene C=CR2 unit, the two R groups are same then there is no cis−trans isomerism.
R−CH=CH−R , this type of alkene only exist cis−trans isomerism.
