Question
Question: Given below is a schematic diagram showing Mendel’s experiment on sweet pea plants having axial flow...
Given below is a schematic diagram showing Mendel’s experiment on sweet pea plants having axial flowers with round seeds (AARR) and terminal flowers with wrinkled seeds (aarr). Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
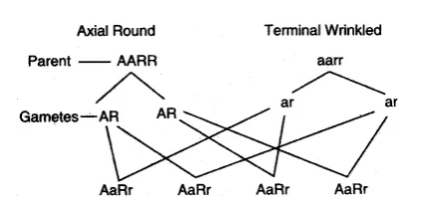
A. Give the phenotype of F1 progeny.
B. Give the phenotype of F2 progeny produced upon by self-pollination of F1 progeny.
C. Give the phenotype ratio of F2 progeny A.
D. Name and explain the law induced by Mendel on the basis of the above observation.
Solution
Dihybrid cross is used for observing inheritance of two different traits. The two plants crossed differ in genes of two traits that are needed to be observed. In this case, two traits observed together are flower colour and shape of seeds. Axial flower and round seeds are dominant traits and terminal flowers and wrinkled seeds are recessive traits.
Complete answer:
a) When plant with axial flowers with round (AARR) flowers is crossed with the plant having terminal flowers with wrinkled seeds (aarr), the F1 progeny produced is heterozygous for both the traits (AaRr) but the dominant trait is expressed and all plants have axial flowers and round seeds. Hence, the phenotype is axial flowers with round seeds.
b) When F1 generation (AaRr) are self-pollinated plants, then each trait is expressed independently giving axial flowers with round seeds, axial flowers with wrinkled seeds, terminal flowers with round seeds and terminal flowers with wrinkled seeds. Both dominant and recessive traits are expressed.
c) In F2 progeny, the phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1. 9 plants have both the traits in the dominant form (AARR), 3 plants have first dominant allele and second recessive trait (AArr), 3 plants have second dominant and first, recessive allele (aaRR) and 1 plant have both recessive alleles (aarr).
d) The cross is a dihybrid cross which considers two traits at a time and according to the ‘Law of independent assortment’ given by Mendel, which states that genes or factors controlling different traits assort independently of each other at the time of gamete formation.
Note: The three laws proposed by Mendel play an important role in determining the trait of an organism. They are:
i. Law of dominance
ii. Law of segregation and
iii. Law of independent assortment
