Question
Question: Given,\[1,3 - \] butadiene has A.sp and \[s{p^2}\] hybridized C-atoms B.sp, \[s{p^2}\] and \[s{p...
Given,1,3− butadiene has
A.sp and sp2 hybridized C-atoms
B.sp, sp2 and sp3 hybridized C-atoms
C.only sp2 hybridized C-atoms
D.only sp hybridized C-atoms
Solution
We need to know that hybridization is the method of mixing two atomic orbitals having the same energy levels, and there is a formation of degenerated new molecular orbitals. It is explained on the basis of quantum mechanics. In the time of hybridization, the atomic orbitals with similar energy will be mixed. In the case of sp2 –orbitals, one s-orbital and two p-orbitals are mixing.
Complete answer:
The 1,3−butadiene has only sp2 hybridized C-atoms. 1,3−butadiene is a chemical compound having the molecular formula CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2. And here all carbon atoms have sp2 hybridization. Let’s see the structure,
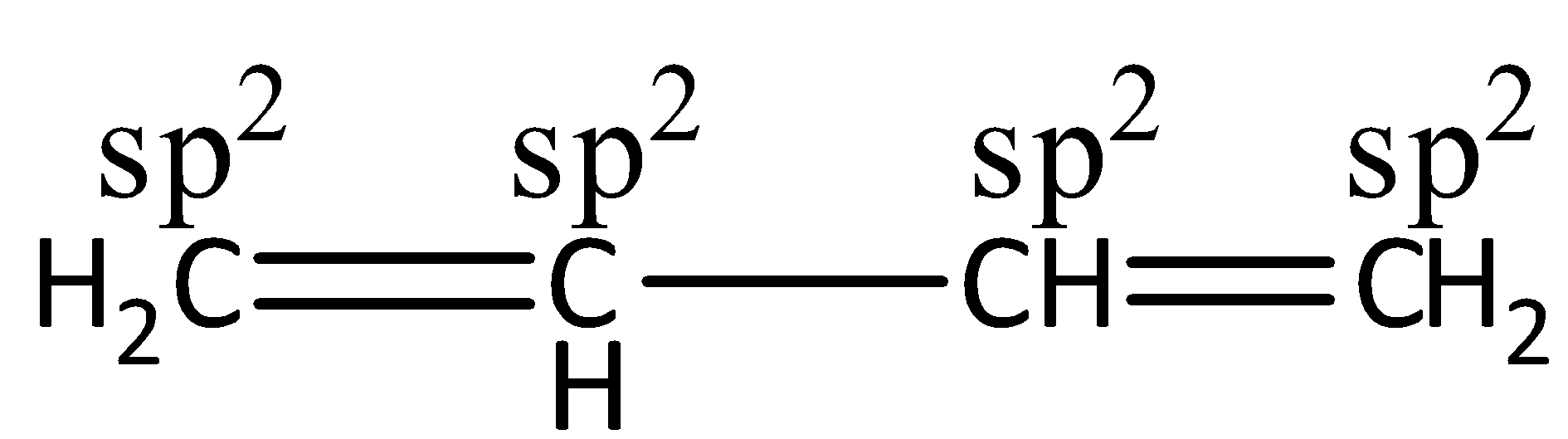
The hybridization is used for the explanation of molecular geometry. And the VSEPR theory is used for the prediction of geometry. The VSEPR theory is also known as Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. It defines the geometry of individual molecules by using the number of pairs of electrons present around the central atoms. For example, for sp hybridization, the shape is linear, sp2→ trigonal planar, sp3→ tetrahedral, sp3d→ trigonal pyramidal and sp3d2→ octahedral. Hence, we can say that the definite shape of the compound can be found by the combination of VSEPR theory and hybridization.
Note:
We need to know that the hybridization of orbital hybridization is a method of mixing atomic orbital with new hybrid orbitals having different shapes, energy than the atomic orbital components. In the case of sp2 and sp3 hybridization expresses the number of s orbital and p orbital and there is a formation of new degenerate hybrid orbitals. And hybridization is related with molecular geometry.
