Question
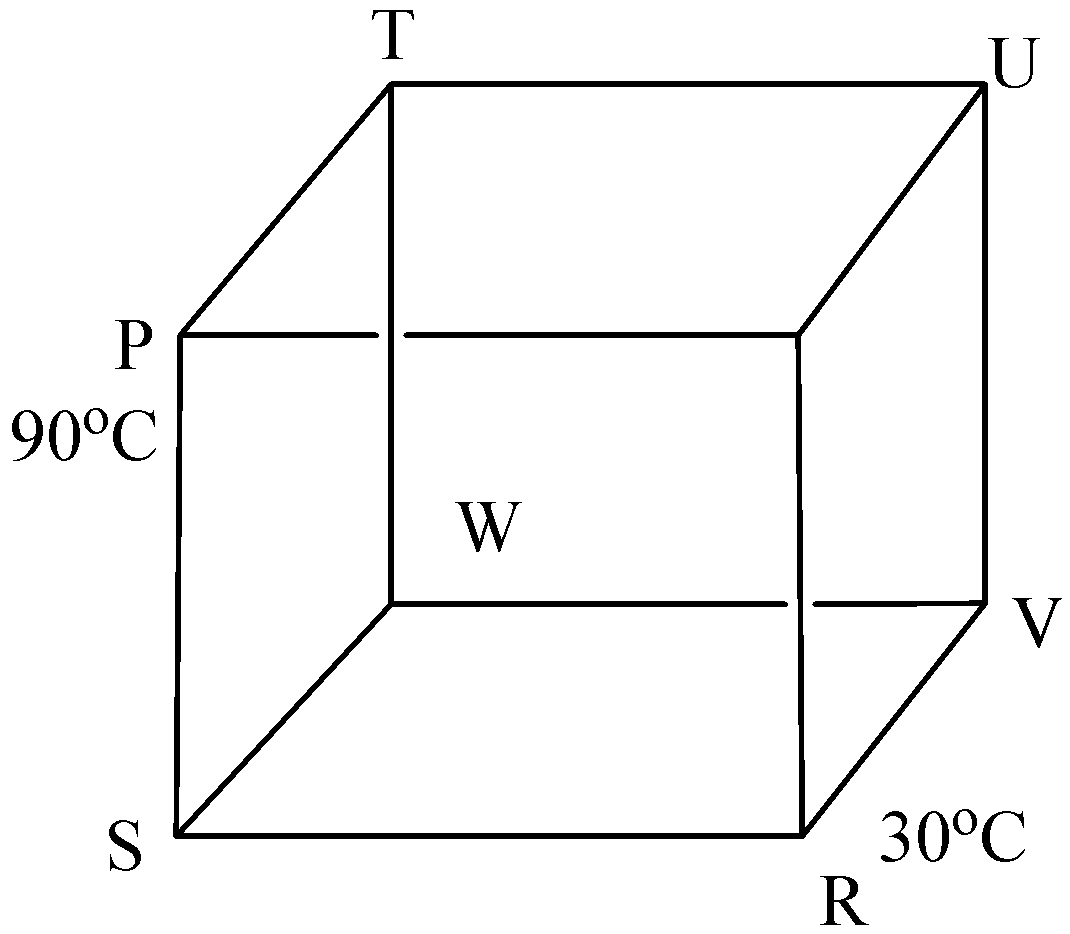
Question: Given,\[12\] Identical rods made of the same material are arranged in the form of a cube. The temper...
Given,12 Identical rods made of the same material are arranged in the form of a cube. The temperature of 'P' and 'R' are maintained at 90∘C and 30∘C respectively. Then the temperature of point V, when steady state is reached is:
A.65∘C
B.60∘C
C.20∘C
D.50∘C
Solution
According to thermodynamics, in a steady state condition, the physical process or the system remains constant after the transformation or change. Which means, it is an unchanging condition. For example, if we take a chemical mix with different properties, and that chemical mix keeps that same properties, even after adding a change agent. And this is the example for steady state.
Complete answer:
The temperature of V is not equal to 65∘C. Hence, option (A) is incorrect.
At steady state, the temperature does not become 60∘C. Hence, the option (B) is incorrect.
The temperature of point V is not equal to 20∘C. Hence, option (C) is incorrect.
Given, the temperature of P and R rods are 90∘C and 30∘C respectively. And here all the rods are identical. Therefore, the thermal conductivity of all the rods are equal. And it passes the same amount of heat through all the rods.
Let us consider the resistance of each rod is 1Ω
By calculation, we got the value of net resistance between P and R is 43Ω
We need to find out the current which passed through P and coming out from R. Therefore,
I=RV
According to current electricity, V is equal to the difference between the temperature of P and R rods. And R is the resistance between P and R, that is 43Ω. Substitute the values in above equation,
I=4390−30
=4360
⇒I=360×4
On simplification we get,
I=80Ω
So, 80Ω of current will enter into P and exit from R. We know P and R maintain some potential and that is, 90V and 30V respectively. And the same current will pass through P and R.
Next we can find out the temperature of V in terms of voltage. Where resistance of V is equal to one and current passes through V is equal to 10Ω, voltage is equal to 60V.
Hence,
I=(60−10)×1
On simplification we get,
⇒I=50V
Here, the electric current is replaced by heat and the temperature of point V, when steady state is reached, is equal to 50∘C.
Hence, the option (D) is correct.
Note:
We need to know that in the case of steady state, the state variables are always equal to the same or constant. And there will not be any change in their physical state, if we add any changing agent. And the steady state can be kept up by balancing the rate of substrate. But in the case of an unstable state, the variable should be changed in each interval of time.
