Question
Question: Give the total number of monochloro products (including stereoisomers), which are possible in the Be...
Give the total number of monochloro products (including stereoisomers), which are possible in the Below reaction.
n - Butane Cl2/hv
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Solution
Write the structure of n – butane first. Under the presence of sunlight, dehydrogenation that is removal of possible hydrogen atoms will take place and then additional chlorine that is halogenation will take place. Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas.
Complete Step by step answer:
The structure of n – butane is: CH3CH2CH2CH3.
When Cl2 is added to n- butane in presence of sunlight, halogenation takes place in 3 ways.
n− Butane gives three products i.e. S− 2− chlorobutane, R- 2− chlorobutane and 1− chlorobu- tane when n− Butane is treated with Cl2 in presence of light. Where (S -2 chlorobutane and R -2 chlorobutane) are stereoisomers. One hydrogen atom gets removed from carbon number 1 of n-butane and one Cl2 atom takes its position under the presence of sunlight.
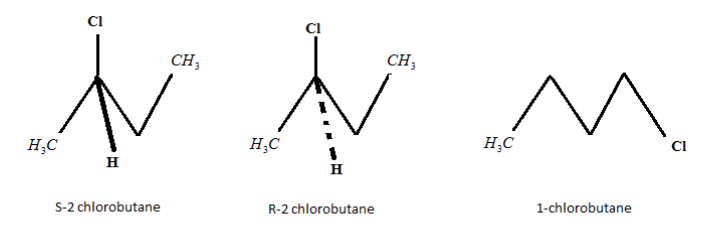
Thus, 1-chlorobutane is formed. Cl2 atom attacks n-butane at second number carbon atom. At this position, 2 stereoisomers are formed, as chlo- rine attacks the compound from the front and back side .The 2 stereoisomers formed are S-2 chlorobutane and R-2 chlorobutane. Hence, the total number of monochloro products (including stereoisomers), which are possible is 3.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional information: Alkanes undergo halogenation reaction through the formation of free radicals as intermediates. The process is known as a free radical mechanism. Thus, halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms in an organic compound by a halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). However, the hydrogen atoms of an alkane may undergo substitution, resulting in a mixture of products.
Note: Students can number the carbon groups from either end in n-Butane, due to the absence of any external group. Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas. Check the direction of attack of chlorine atom during halogenation of alkane.
