Question
Question: Give the schematic representation of the overall view of TCA cycle?...
Give the schematic representation of the overall view of TCA cycle?
Solution
The tricarboxylic acid cycle is also known by the name of Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle which will help you in remembering the name of the starting material and since it is a cycle so the end product is also the starting product. The citric acid cycle helps plants in getting energy to carry out the metabolism required to survive.
Complete answer:
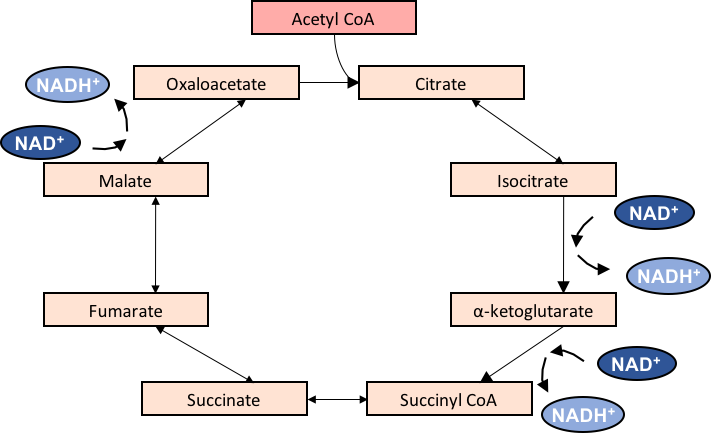
The Krebs cycle starts and the end point is citrate or the citric acid and in between the cycle there are few more organic compounds which are formed so as to release the energy and complete the cycle. The main purpose of the Krebs cycle is the production of energy by breaking down the pyruvate into citrate and eventually again forming the citrate. This cycle requires NADH as the energy source and release NAD+ as the energy to be utilized.
The substrate for the krebs cycle is the pyruvic acid which is transformed into acetyl CoA and this will again get modified into citric acid. if we see the chemical structure then we will see that the pyruvic acid is a 3 carbon structure whereas the citric acid is 6 carbon compounds.
The process of transformation of pyruvate is for providing energy to the cycle for carrying out further changes. The citric acid will begin the cycle by changing into isocitric acid by releasing its one of the carbon molecules as carbon dioxide.
Then this isocitric acid will change into 𝝰ketoglutaric acid by losing a carbon molecule. After this step no loss of carbon molecule occurs and further transformations are into succinyl CoA followed by succinate.
This succinate will then form fumarate followed by the formation of malate. The malate will form the end product of the cycle and the cycle will again start on the addition of acetyl CoA into it.
Note: Though the TCA cycle starts with the citrate but we take the pyruvate as the main source which breaks down and forms the citrate with which the reaction is taking place and providing the energy.
