Question
Question: Give the phenotype and genotype of the \({ F }_{ 2 }\) generation in a monohybrid cross....
Give the phenotype and genotype of the F2 generation in a monohybrid cross.
Solution
Monohybrid cross is used to refer to the cross in which two individuals are crossed to study the inheritance pattern of only one character which can be plant height, seed color, seed shape, pod color, pod shape, etc.
Complete answer:
Phenotype is referred to as the outward physical expression of a gene and genotype is the genetic makeup of the mentioned gene and its alleles.
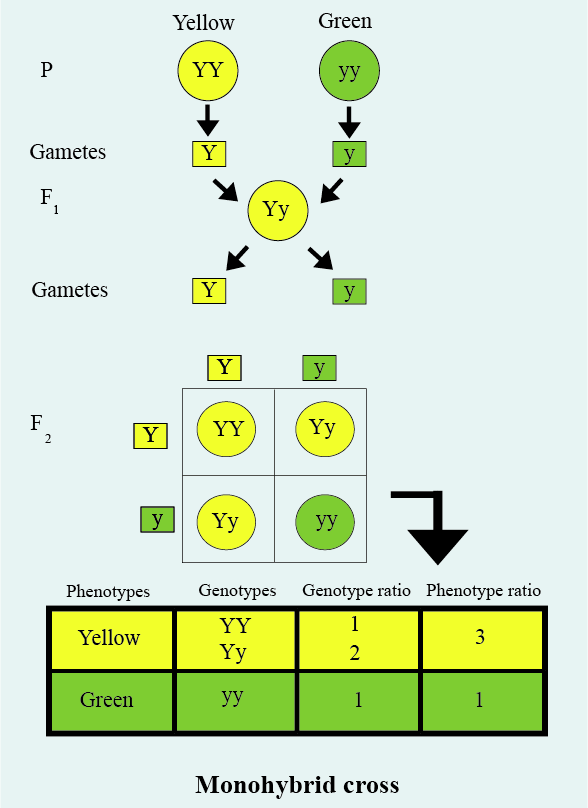
Let us take a monohybrid cross in which the seed color is taken as the character to be studied. The dominant allele gives yellow color and thus is represented by Y and the recessive allele gives green color and is represented by y. When a plant with YY genotype (homozygous dominant) is crossed with another plant having yy genotype (homozygous recessive), the resultant filial or F1 generation will have all yellow seed plants.
When we self pollinate a member of the F1 generation, we see yellow and green seed plants indicating to us that all the members of the F1 generation were heterozygous dominant and thus were able to produce both yellow and green seeds in the next generation.
The Punnett square shown below will help us understand the self-pollination of F1 to produce the F2 generation.
Here we observe that 43 of offsprings produced were having yellow seeds and the rest 1/4 offsprings were having green seeds.
Thus, the phenotypic ratio is 3 (yellow seeds):1(green seeds)
Now if we look closely at the Punnett square, we will see that out of the 3 yellow seed-producing plants, 1 is homozygous dominant and 2 are heterozygous dominant. The green seed-producing plant is homozygous recessive.
Thus, the genotypic ratio is 1 (homozygous dominant): 2(heterozygous dominant): 1 (homozygous recessive)
Note:
- Two laws of Mendel were proposed based on the observations of the monohybrid cross.
- The first law is the law of Dominance and states that in a pair of dissimilar alleles, the dominant allele will express itself over the recessive allele.
- The second law is the Law of Segregation and it states that the pair of alleles segregate during gamete formation and combine again during fertilization.
