Question
Question: Give the conversion: Acetone to 2-Methylpropene...
Give the conversion:
Acetone to 2-Methylpropene
Solution
This conversion is a two-step conversion. In the first step, we can use the reactivity of the ketone functional group to add the required methyl group. Then, we can obtain alkene by removal of small molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Acetone has three carbon atoms in its structure and 2-methylpropene has four carbon atoms. So, there is one carbon more in the product. So, we will need to add a carbon atom in the reactant. Also, the final product is an alkene which we can find from the name of the product that has –ene suffix.
- So, the more reactive functional group in acetone is C=O and we will need to make this group react. We will first do the addition of a methyl group on the carbonyl carbon by Grignard reagent and then, as a result, we will obtain alcohol with four carbon atoms.
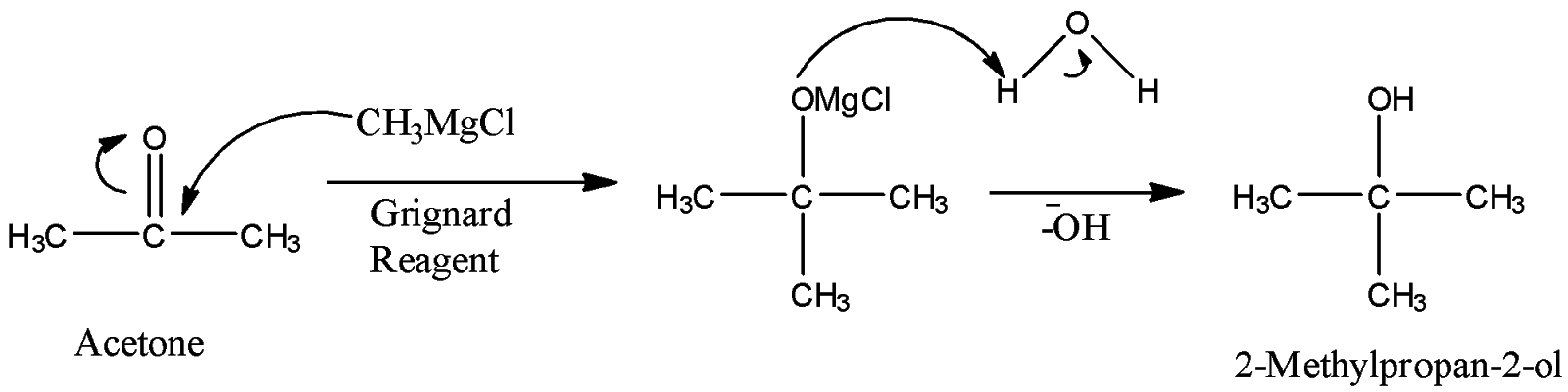
- So, here the methyl group in the Grignard reagent is highly nucleophilic and will attack the electrophilic carbonyl carbon to give an additional reaction and C-O double bond will be broken. Then, water workup will give us alcohol, 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
- Now, we can see that it is tertiary alcohol as the carbon-bearing hydroxyl group is attached with other three carbons. So, we can easily prepare an alkene from tertiary alcohol by dehydration.
- For dehydration reaction, we need to use a dehydrating agent. Sulphuric acid is a good dehydrating agent. So, we will use this reagent for this conversion.
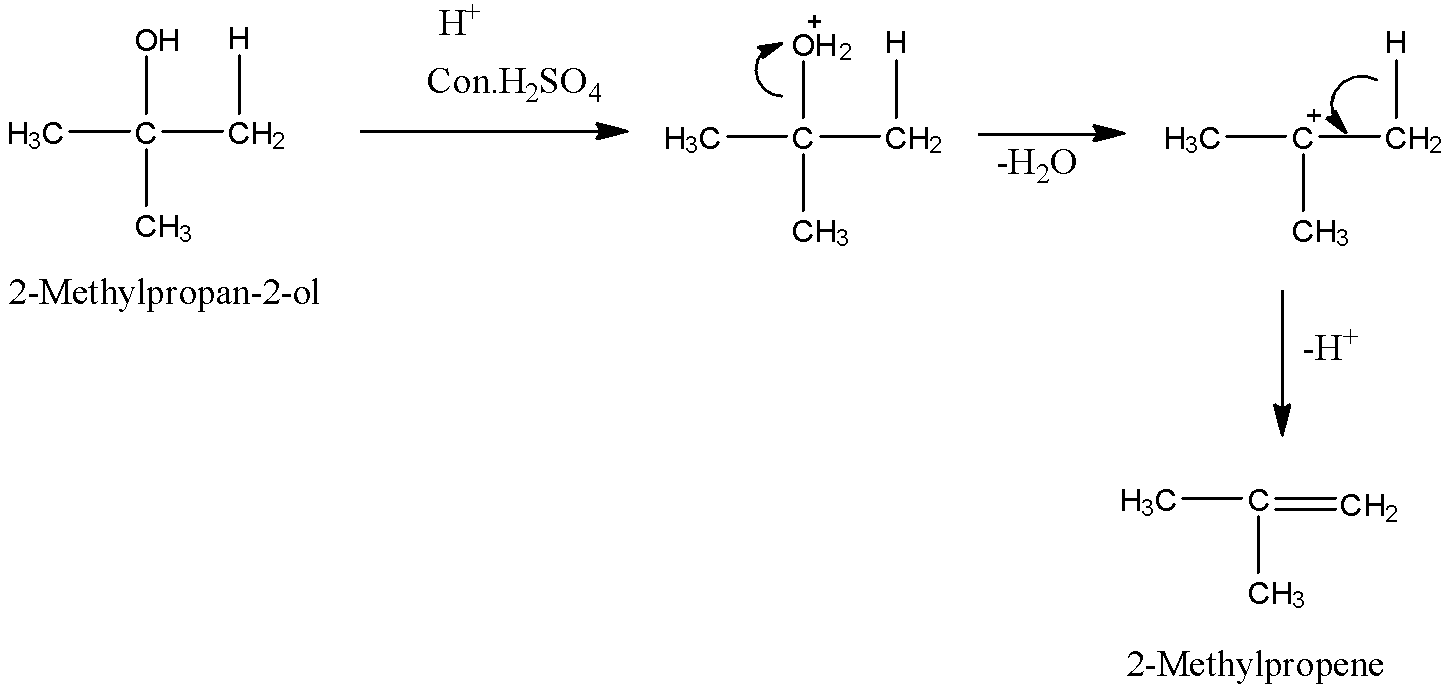
- So, we can see that hydroxyl group and a hydrogen atom from its adjacent carbon gets removed in the form of water and as a result, we obtain an alkene, 2-Methylpropene which is the required product.
Note: Remember that sulphuric acid cannot react with acetone. So, the order of the steps is very important as different functional groups have different reactivity towards different reagents. We can also use organo-lithium reagent in place of Grignard reagent here.
