Question
Question: Give the advantages and disadvantages of potentiometric titration....
Give the advantages and disadvantages of potentiometric titration.
Explanation
Solution
Potentiometric titration is a method of determining concentration of unknown solute in a solvent under the influence of potential applied between two electrodes.
Potentiometric titration involves two types of basic electrodes: one is known as indicator electrode and another one is standard electrode.
Complete answer:
Some basic disadvantage and disadvantage of Potentiometric titration includes-
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|
| Simple titration method | More complex than simple acid- base titration |
| Require less amount of time for completion of process | It requires special assembly to carry out process |
| This does not require any indicator | Galvanic cell is used to carry out the process |
| End result of the reaction is easily visible. | Require electrodes of metal like silver, hydrogen. |
| Reaction is not interfered by reaction poison like mercury etc. | Overall cost of the process is high |
| Equilibrium of the reaction achieved quickly | Continuous supply of electricity is mandatory |
| Accuracy of the end result is good. | Electrolyte used in the reaction must be freshly prepared. |
| This titration can be performed even in the presence of a small amount of solute whose concentration is to be determined. | Variation in electrolyte pH alters the result of titration. |
| This reaction is helpful to determine the end result of the titration when there is lack of some suitable indicator for the reaction. | There is always a need for some standard electrode like calomel electrode, hydrogen electrode, or other metal chloride electrode. |
| This titration may become automated by using computers to get self-generated data. | Contamination during electrolyte preparation may cause deflection from actual results. |
Note:
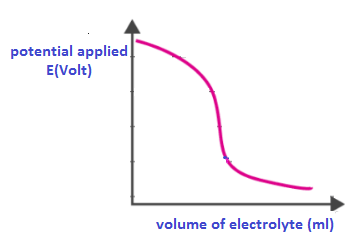
End point of the titration is determined by calculating the potential drop in the cell.
A graph is plotted at the last between potential applied and volume of electrolyte solution.