Question
Question: Give graphical representation of cell cycle?...
Give graphical representation of cell cycle?
Solution
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
In the cell division process, a parent cell divides to produce two or more daughter cells.
Cell division is considered as a part of the cell cycle.
Complete answer:
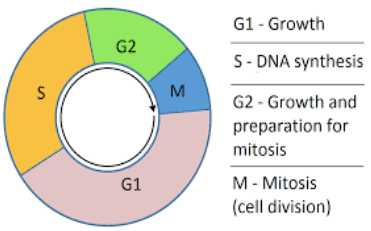
A cell cycle can be defined as changes taking place in a cell during its growing phase.
Maximum time is spent by the cell in the interphase where it grows, replicates its chromosomes, and starts preparing for cell division. After this, it undergoes mitosis, thus completing its division.
In the G1 phase , the cell grows and increases in size (growth 1).
In S phase DNA replication takes place.
In G2 it prepares to divide.
It finally divides into mitosis, or M phase.
Phases
M phase is itself composed of two tightly coupled processes: mitosis, in which the cell's nucleus divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cell's cytoplasm divides, forming two daughter cells. Each phase gets activated on completion of the previous one.
Non dividing cells go to the G0 phase. It is also called the quiescent stage.
Interphase
In Interphase, changes are seen in a newly formed cell and its nucleus before dividing again.
Interphase further has G1, S, and G2, followed by the cycle of mitosis and cytokinesis. The cell's nuclear DNA contents are duplicated during S phase.
The G1 phase is also called the growth phase.
During this phase, the biosynthetic activities of the cell occur at a faster pace.
In the G1 phase, three things are possible:
a.To continue cell cycle and enter S phase
b.stop cell cycle and enter G0 phase for undergoing differentiation.
c.Become arrested in G1 phase hence it may enter G0 phase or re-enter cell cycle.
The ensuing S phase starts when DNA synthesis commences; when it is complete, all of the chromosomes have been replicated, i.e., each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. Thus, during this phase, the amount of DNA in the cell has doubled and the number of chromosomes are unchanged.
G2 phase (growth)
Rapid growth is seen in G2 phase occurs after DNA replication. Protein synthesis also occurs. During this phase microtubules start forming a spindle.
The M phase consists of nuclear division (karyokinesis).
M phase is very complex and efficiently regulated.
The sequence of events is divided into phases, corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next.
These phases are sequentially known as:
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Mitosis happens when an eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets in two nuclei. The chromosomes pair condense and attach to microtubules which then stretch the sister chromatids to opposite sides of the cell.
After Mitosis, Cytokinesis occurs. Mitosis and cytokinesis play a vital role for the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell. This accounts for approximately 10% of the cell cycle.
Note: All multicellular organisms use cell division for growth, maintenance and repair of cells and tissues.
Unicellular organisms use this process to reproduce. So cell cycle is the fundamental process by which a cell matures, synthesises DNA and divides to form daughter cells. Somatic cells divide regularly.
