Question
Question: Give an account of carboxylation ( \({ CO }_{ 2 }\) fixation) stage of the Calvin cycle?...
Give an account of carboxylation ( CO2 fixation) stage of the Calvin cycle?
Solution
Carboxylation ( CO2 fixation) stage of the Calvin cycle is part of the dark reaction that is a stage of photosynthesis not dependent on the light. It utilizes the products formed in the light reaction to synthesize food i.e sugar.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is an integral process in the ecosystem to produce carbohydrates from CO2 and water with the help of sunlight and chlorophyll. It has two stages- light reaction and dark reaction. The light reaction takes place in the presence of light because they have to produce energy-rich ATP molecules and reduced coenzymes NADPH.
- This assimilatory power is utilized in the biosynthetic phase of the dark reaction of photosynthesis where finally the glucose is formed.
- The light reaction occurs in the grana of chloroplast wherein the dark reaction occurs in its stroma.
- Calvin Cycle is a part of the dark reaction in the mechanism of photosynthesis. The dark reaction was discovered by FF Blackman in 1905 but later studied in detail by Calvin, Benso, and J Bassham. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1961 for this work.
- It involves three stages namely-Carboxylation, Reduction, and Regeneration.
- In the first stage of the Calvin cycle i.e Carboxylation which is the addition of the CO2 to an acceptor. Here, the incoming CO2 is incorporated into a five- carbon compound Ribulose- 1,5- bisphosphate (RuBP).
- This reaction is catalyzed by RuBisCO, the product of which is a six- carbon intermediate that immediately splits into a stable organic intermediate i.e two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate.
- Thus, for every three molecules of CO2 entered in a plant cell, there are six molecules of 3- phosphoglycerate formed.
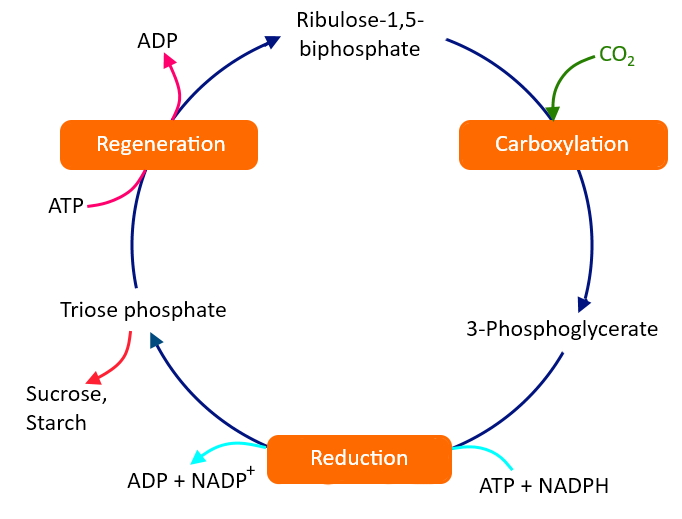
Fig: Calvin Cycle
Note:
- RuBisCO or RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase is the most abundant protein in the chloroplast and also in the Earth.
- The active site of RuBisCO is the same for carboxylation and oxygenation i.e it can react with both CO2 and O2. But the affinity for CO2 is more.
- C3 plants include alfalfa, oats, tobacco, etc.
