Question
Question: Geometry of xenon oxyfluoride \( \left( XeO{{F}_{4}} \right) \) is...
Geometry of xenon oxyfluoride (XeOF4) is
Solution
Hint : We know that both hybridization and VSEPR (Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory) theory together helps in determining the shape and geometry of the molecule. The central atom values must be added to obtain valence shell electron pair number (VSEPR).
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory which is also abbreviated as VSEPR theory. In this theory, the pair of valence electrons will always have some repulsion between them and therefore they will tend to arrange themselves in a manner where the repulsion between the valence electrons is minimum. Total number of electrons present in the outermost shell of the central atom must be counted. The total numbers of electrons that belong to the other atom are used in bonding with the central atom and it should also be counted. Hybridization is the intermixing of a particular number of atomic orbitals to form an equal number of new orbitals which have the same shape and energy. It is used to determine the shape of the molecule. The new orbital that is formed are also known as hybrid orbitals. During hybridization, the atomic orbitals with different characteristics are mixed with each other.
The molecular structure of (XeOF4) will be: It will form a square pyramidal structure. The central atom will use its s−orbitals its p−orbital and as many of its d−orbitals as needed to mix together to make the hybrid orbitals. So, for XeOF4,Xe will need its s orbital, all three of its p−orbitals, and two of its d−orbitals and its hybridization state will be sp3d2/d2sp3.
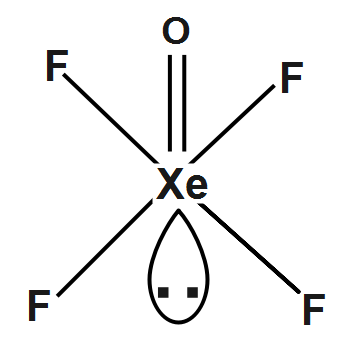
Therefore, Xenon oxyfluoride (XeOF4) is the square pyramidal shape.
Note :
Remember that if it fails to explain the isoelectronic species. These species may vary in shape and they have the same number of electrons. It does not explain about transition metals. The structures of such compounds are not described correctly by this theory.
