Question
Question: Gene regulation governing lactose operon of _E. coli_ that involves the lac I gene product is?...
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E. coli that involves the lac I gene product is?
Solution
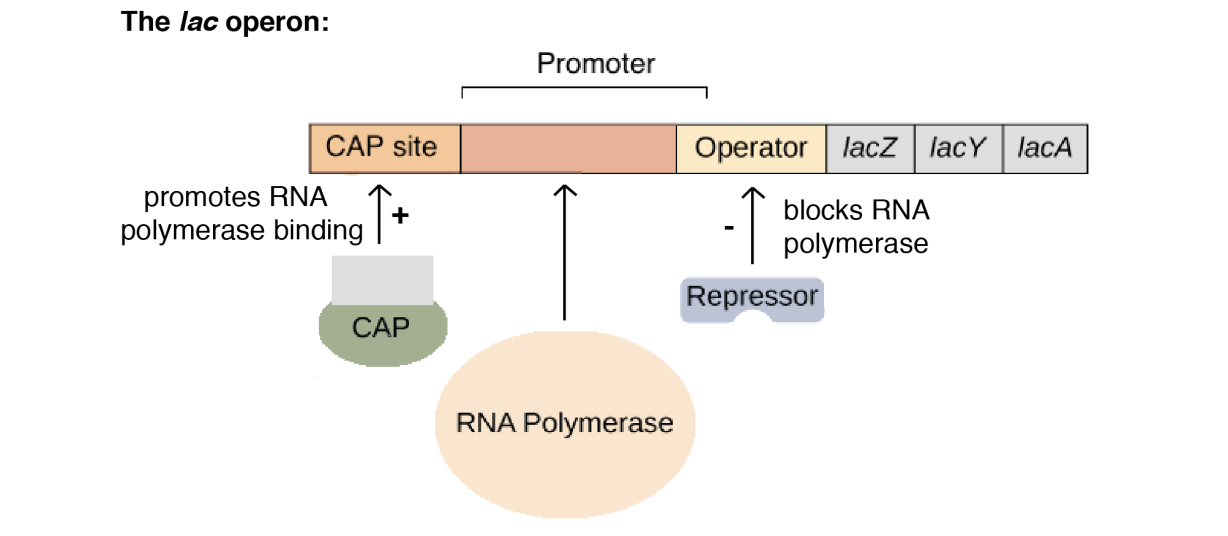
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E. coli that involves the lac I gene product is negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription. Control of gene expression in lac operon is negative as it is turned off normally due to the binding of the repressor to the operator region. It is inducible by the presence of inducers such as lactose allolactose. The inducer binds to the repressor and therefore, RNA polymerase can now access the promoter site to initiate transcription.
Complete answer:
The lac operon consists of the following genes -
Structural genes - lac z, lac y, lac a
Operator gene
Promoter gene
Regulator gene (i)
The operon is switched off when a repressor protein produced by regulatory or inhibitor gene binds to the operator gene. RNA polymerase gets blocked, so there would be no transcription.
Repressor protein + Operator gene → Switched off
Regulation of lac operon by a repressor is referred to as negative control or regulation.
If lactose is provided in a growth medium of the bacteria, the lactose is transported into the cells through the action of permease. A very low level of expression of lac operon has to be present in the cell all the time, otherwise, lactose cannot enter the cells. In the presence of an inducer such as lactose or allo-lactose, the repressor is inactivated by interaction with the inducer. This allows RNA polymerase access to the promoter & transcription proceeds.
Inducer (Lactose) + Repressor → Switched on
Note:
In negative inducible operons, a regulatory repressor protein is normally bound to the operator, which prevents the transcription of the genes of the operon. The lac operon is a positively inducible system. An example of a repressible system is the trp operon or tryptophan operon.
