Question
Question: Fruit color in squash is an example of a. Recessive epistasis b. Dominant epistasis c. Complem...
Fruit color in squash is an example of
a. Recessive epistasis
b. Dominant epistasis
c. Complementary genes
d. Inhibitory genes
Solution
Fruit squash can be found in white with green or yellow color. What color the fruit will majorly depend on genetics. The color selection follows a dihybrid cross which is crossed over between a homozygous pair of alleles (white and yellow) and homozygous pair of alleles (white and green).
Complete answer:
Epistatic genes are genes that control the expression of alleles. They can be divided into two types that are Dominant epistatic genes and recessive epistatic genes.
Complementary genes are the genes that are present on different loci that require each other to express certain characteristics.
Inhibitory genes are the ones that prevent the expression of another gene.
In squash, the white color gene is dominant over genes of yellow and green color. The dihybrid cross of dominant epistatic alleles is given below.
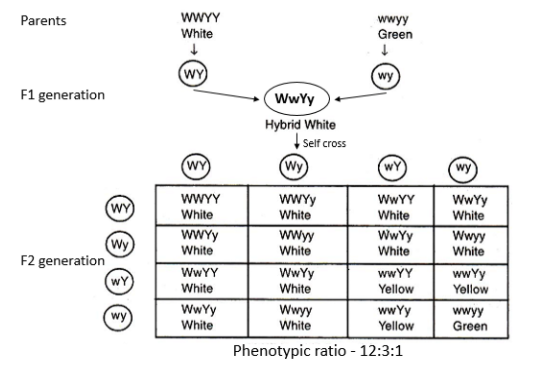
In the above pictorial representation, we can observe that the white color allele is dominant over green and yellow color alleles. The white color allele is expressed even in the heterozygous condition. The majority of zygotes will produce white color fruit. Here the gene contains alleles for both white and yellow or green color but the white color allele masks the effect of green or yellow color’s alleles. This is called the dominant epistasis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The epistatic genes decide whether the alleles will be expressed or not. The other example of epistatic genes is genes that determine skin color in humans. Epistatic genes can be hereditary. Sometimes due to epistasis, genes are present but do not get expressed.
