Question
Question: Four capacitors of capacitances \(C,2C,3C\text{ and }4C\) are connected as shown. At \(t=0,\) S is c...
Four capacitors of capacitances C,2C,3C and 4C are connected as shown. At t=0, S is closed. Find the charge flowing through connector AB.
A.5CE
B.3CE
C.2CE
D.6CE
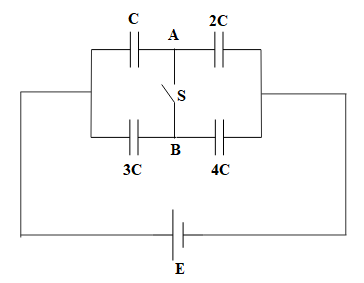
Solution
We shall first analyze the two situations separately when the switch is closed and when it is open. Then we will find the total capacitance of the arrangement shown and simultaneously the charge associated with it. Further, according to the polarity of the plates of the capacitors, the charge in connector AB will be calculated.
Complete answer:
The charge (Q), voltage (V) and capacitance of the capacitor are related as:
Q=CV ……………. Equation (1)
Initially when S is closed, the circuit is as follows:
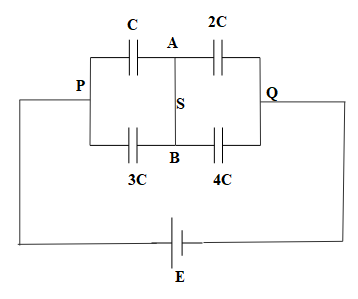
The capacitors with capacitances C and 2C are in series with each other and their resultant capacitance, Ceq1 is given as:
Ceq11=C11+C21⇒Ceq11=C1+2C1⇒Ceq11=(2C)(C)2C+C
⇒Ceq1=3C(2C)(C)⇒Ceq1=32C
Using equation (1),
Charge in this upper branch is, Q1=CV
⇒Q1=(32C)E
∴Q1=32CE
Also, the capacitors with capacitances 3C and 4C are in series with each other and their resultant capacitance, Ceq2 is given as:
Ceq21=C11+C21⇒Ceq21=3C1+4C1⇒Ceq21=(3C)(4C)4C+3C
⇒Ceq2=7C(3C)(4C)⇒Ceq2=712C
Using equation (1),
Charge in this upper branch is, Q2=CV
⇒Q2=(712C)E
∴Q2=712CE
We shall now analyze the charges on the plates of the capacitors. They are as depicted in the diagram:
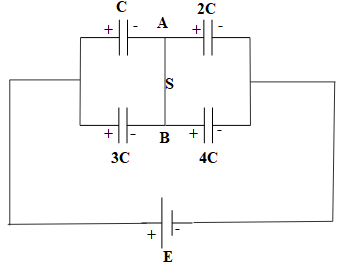
When S is closed, capacitors C and 3C are connected in parallel,
Their equivalent capacitance is given as:
Ceq=C+3C
⇒Ceq1=4C
Also, capacitors 2C and 4C are connected in parallel,
Their equivalent capacitance is given as:
Ceq=2C+4C
⇒Ceq2=6C
The circuit is now transformed as:
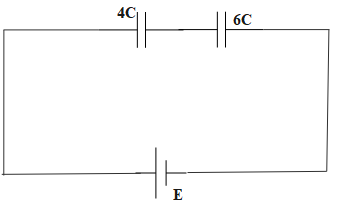
Thus, the total capacitance is:
Ceq1=Ceq11+Ceq21⇒Ceq1=4C1+6C1⇒Ceq1=(4C)(6C)6C+4C
⇒Ceq=10C(4C)(6C)⇒Ceq=1024C
∴Ceq=2.4C
Using equation (1), the total charge is Q=2.4C(E)
Since 4C and 6C capacitors were in series, therefore both of them acquire charge 2.4CErespectively.
However, 4C capacitance consists of capacitors C and 3C in parallel.
⇒QC+Q3C=2.4CE ……………………. Equation (2)
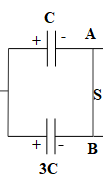
Therefore, VC=V3C,
⇒QCC=Q3C3C⇒Q3C=3QC
Combining equation (2) with this, we get
⇒QC+3QC=2.4CE⇒4QC=2.4CE⇒QC=0.6CE
Similarly, 6C capacitance consists of 2C and 4C,
⇒Q2C+Q4C=2.4CE ……………………. Equation (3)
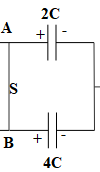
Therefore, V2C=V4C,
⇒Q2C2C=Q4C4C⇒Q4C=2Q2C
Combining equation (2) with this, we get
⇒Q2C+2Q2C=2.4CE⇒3Q2C=2.4CE⇒Q2C=0.8CE
The charge at junction A is −QC+Q2C=−0.6CE+0.8CE=0.2CE
Thus, the charge in connector AB is 0.2CE=102CE=5CE
Therefore, the correct option is (A) 5CE
Note:
Capacitors C and 3C are connected with the positive terminal of the battery, therefore, their left plate will acquire a positive charge and their right plate will acquire negative charge. Likewise, capacitors 2C and 4C are connected with the negative terminal of the battery, therefore, their right plate will acquire negative charge and their left plate will acquire positive charge.
