Question
Question: Formation of (P) is known as Tollens reaction. Identify the total number of stereoisomers for ‘Q’. ...
Formation of (P) is known as Tollens reaction. Identify the total number of stereoisomers for ‘Q’.
CH3CH2CHO+3HCHCONaOHΔPCH3CHO(1eq)H+Q
Solution
The compounds which are having chiral centers in their structures are going to exhibit stereoisomerism. The formula to calculate the number of stereoisomers in an achiral compound is as follows.
Number of stereoisomers = 2n
Here n = number of chiral centers.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is given to identify the product ‘P’ and make the reaction of P with acetaldehyde. We have to find the number of stereoisomers in the compound Q.
- The chemical reaction contains two steps.
Step-1:
- In the question it is given that the formation of P is due to the Tollen’s test means the reactant is an aldehyde. Because aldehydes only responds to Tollen’s test. Alcohols are not going to respond to Tollens test.
- The chemical reaction of propionaldehyde with three moles of formaldehyde is as follows.
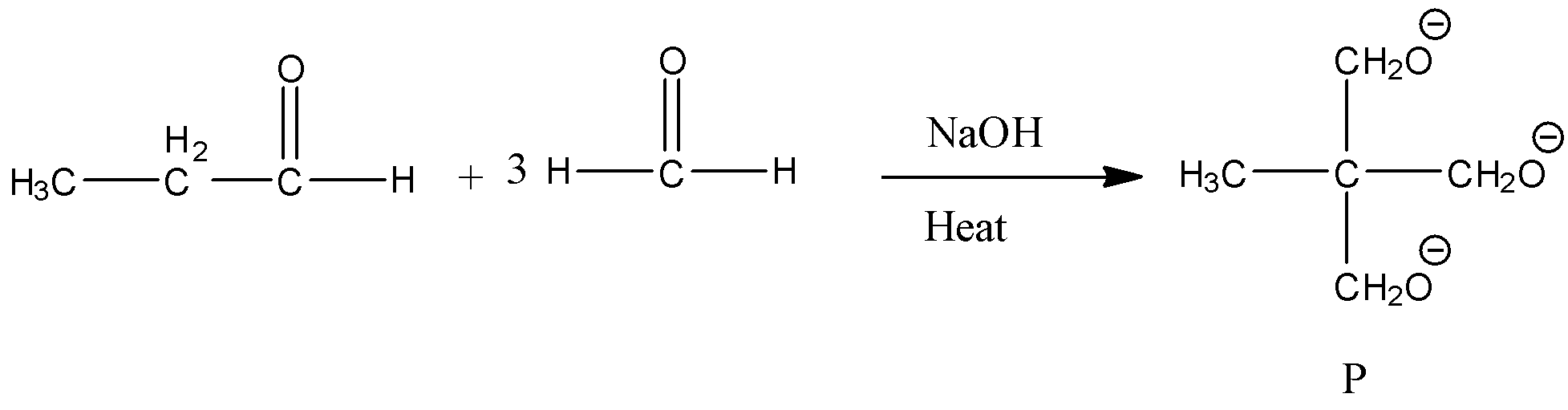
- In the above chemical reaction one mole of propionaldehyde is going to react with three moles of formaldehyde and forms one mole of ‘P’ as the product.
Step-2:
- In the step-2 the product in the above chemical reaction ‘P’ is going to react with one mole of acetaldehyde in the presence of acid and forms the product B and the chemical reaction is as follows.
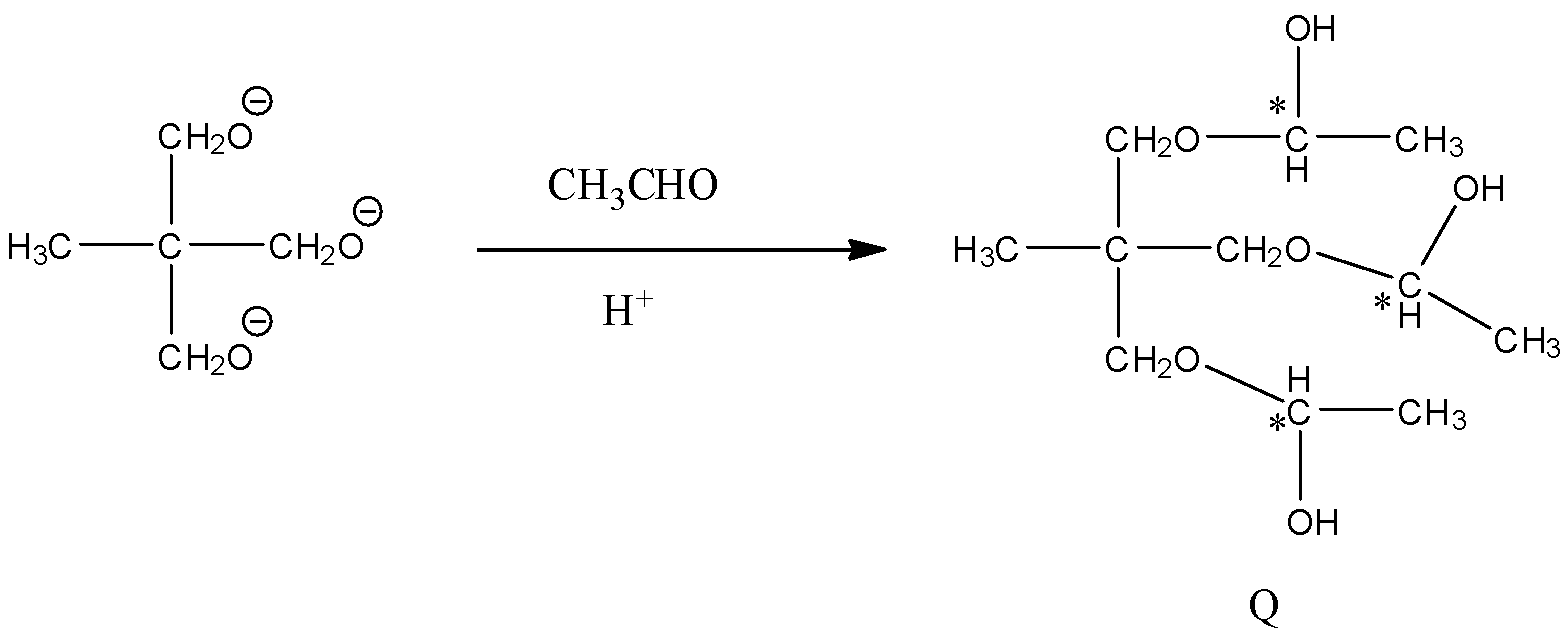
- From the above chemical reaction we can find that the number of chiral centers in the product Q is three and they are represented with star symbols.
- Therefore the number of stereoisomers which are going to be formed by the product B is 23=8.
So, the number of stereoisomers formed by the product B are 8.
Note:
The carbon which contains four different substituents in a molecule then the carbon is called chiral center. Chiral carbon containing molecules are optically active in nature means they rotate the polarized light to either the right or left side.
