Question
Question: For \(Zn(s)|ZnC{{l}_{2}}(aq)|C{{l}^{-}}(aq)|C{{l}_{2}}(g)|C(s)\) According to the above cell diag...
For Zn(s)∣ZnCl2(aq)∣Cl−(aq)∣Cl2(g)∣C(s)
According to the above cell diagram the electrochemical cell described, the reaction at anode is:
a. Zn→Zn2++2e−
b. Zn2++2e−→Zn
c. Cl2+2e−→2Cl
d. 2Cl−→Cl2+2e−
Solution
A galvanic cell contains various elements within it which react with each other in a solution where the cell is placed. These are redox reactions and the galvanic cell converts the energy of these redox reactions into electrical energy. There is an anode and a cathode where reactions take place.
Complete step by step answer:
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell in which various elements on anode and on cathode react to perform half oxidation and half reduction reactions on cathode and anode respectively and this redox reaction energy due to electron transfer is used by the galvanic cell to produce electrical energy. This transfer of electrons through a wire helps to produce electrical energy which is used for various purposes.
In the setup for galvanic cell circuits the anode is the electrode where oxidation reaction takes place and the metal loses electrons and cathode is the electrode where reduction reaction takes place and the electrode gains electrons. This chemical energy produced is converted into electrical energy. It has an external circuit which involves wires attached to the electrodes and the internal circuit which involves the movement of electrons. The circuit has two half cells which contain electrode and electrolyte each. A salt bridge is used to complete the circuit and it maintains neutrality between the two half cells.
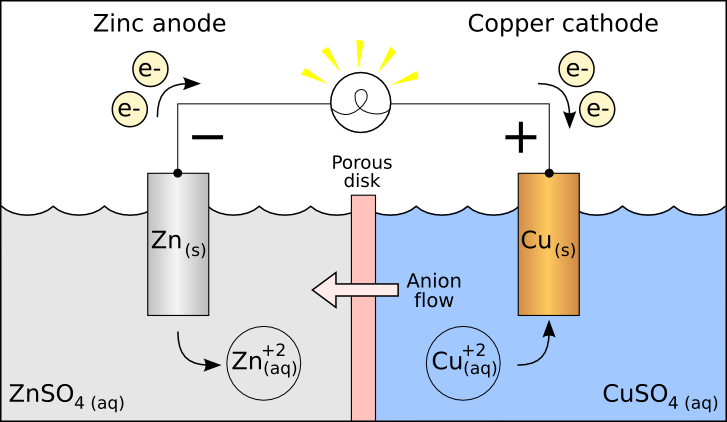
For the given question, the answer is option a.
In the cell diagram the left electrode is anode where oxidation takes place and the right electrode is cathode where reduction takes place, the zinc anode loses electrons and Zn is oxidised so the reaction on anode is
Zn→Zn2++2e−
Note:
The energy from combustion of fuels like hydrogen, methane and more are converted by galvanic cells into electrical energy and these cells are known as fuel cells. These fuel cells are 75 more efficient and are pollution free devices. They are a constant source of energy and are light in weight.
